
IMF: RUSSIA IS BETTER
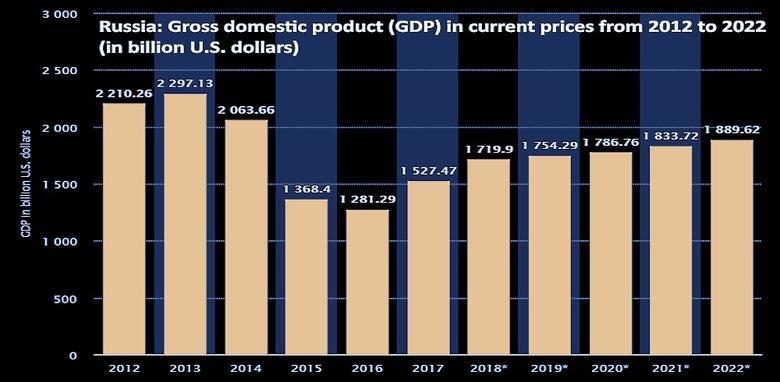
IMF - Russia's economy is recovering from the 2015–16 recession, thanks to the authorities' effective policy response and higher oil prices. Output increased by 1.5 percent in 2017 on the back of robust domestic demand, but short of expectations. Inflation has fallen well below the CBR's 4 percent target since July 2017, driven by a weaker-than-expected recovery, tight monetary policy, as well as temporary effects on food and energy prices.
Growth is projected at 1.7 percent in 2018, supported by rising credit and disposable incomes. Headline inflation is projected to bounce back during the second half of 2018 to 3.5 percent at year-end, supported by the ongoing domestic demand recovery, passthrough from the recent ruble depreciation, and the fading of temporary factors. The medium-term outlook remains muted, due to structural bottlenecks and the lingering impact of sanctions. Absent structural reforms, growth is expected to settle around 1.5 percent, while monetary policy stabilizes inflation around 4 percent by end-2019. The main risks to the outlook stem from geopolitical tensions as well as the new government's policy plans.
Executive Board Assessment
Executive Directors agreed with the thrust of the staff appraisal. They commended the authorities for establishing a strong macroeconomic policy framework that has strengthened economic resilience. Directors noted that despite the ongoing recovery, the medium‑term outlook remains subdued. This reflects uncertainty stemming from geopolitical tensions and shifting global trade and financial conditions. The large footprint of the state, governance and institutional weaknesses, and insufficient infrastructure constitute structural reform priorities. Directors emphasized the importance of implementing structural reforms to boost productivity and the supply of labor and capital to enhance medium‑term growth.
Directors agreed that the fiscal rule helps shield the economy from fluctuations in oil prices and anchors fiscal policy. They emphasized the importance of preserving the hard‑won credibility of the macroeconomic policy framework. Directors encouraged continued fiscal consolidation to rebuild buffers and reach a position consistent with sharing equitably Russia's natural resources with future generations.
Directors welcomed the authorities' plans to boost spending on health, education, and infrastructure, with most emphasizing that this could be achieved within the confines of the fiscal rule. They supported the authorities' plans for parametric pension reform, which could help to offset negative demographic trends. Directors called for better targeting of expenditure on social assistance and strengthening tax compliance and reducing tax expenditures. They encouraged the authorities to engineer a growth‑friendly shift from social security contributions to consumption taxes which could incentivize labor supply, reduce labor informality, and attract new investment.
Directors welcomed the Central Bank of Russia's (CBR) plans to maintain its gradual and data‑driven approach in setting monetary policy, as inflation expectations are not yet firmly anchored and risks to the inflation outlook have increased. They broadly agreed that further monetary easing could be appropriate if headline inflation remains below the 4 percent target and underlying inflationary pressures stay low. Continued efforts to refine the CBR's communications strategy were encouraged.
Directors commended the progress made to restructure the banking sector. However, they noted last year's failure of several large banks and pointed to significant shortcomings in the sector. In this regard, Directors urged the authorities to complete the cleanup of the banking sector, close the gaps in bank supervision and regulation, including addressing related‑party lending, and further efforts to complete the asset quality evaluations. They underscored the importance of having a credible strategy for returning rehabilitated banks to private hands in a way that is consistent with increasing competition and efficiency. Continued efforts to strengthen the AML/CFT framework were also encouraged.
Directors noted that raising growth requires stronger competition in domestic markets, a leaner state, and a more vibrant private sector. They supported measures to reduce the footprint of the state, particularly in banking and other sectors with limited rationale for public ownership in a gradual manner in line with a strengthened institutional architecture. Directors recommended strengthening transparency, accountability, and governance standards in state‑owned enterprises and the corporate sector more generally to improve the business environment. They noted that the authorities could accelerate productivity growth by persisting with their efforts to strengthen competitiveness, promote trade integration, and further diversify exports.
It is expected that the next Article IV consultation with the Russian Federation will be held on the standard 12‑month cycle.
|
Russian Federation: Selected Macroeconomic Indicators, 2015–19 |
|||||
|
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
|
|
Projections |
|||||
|
Production and prices |
|||||
|
Real GDP |
-2.5 |
-0.2 |
1.5 |
1.7 |
1.5 |
|
Consumer prices |
|||||
|
Period average |
15.5 |
7.1 |
3.7 |
2.9 |
4.0 |
|
End of period |
12.9 |
5.4 |
2.5 |
3.5 |
4.0 |
|
GDP deflator |
8.0 |
3.5 |
5.2 |
5.2 |
4.4 |
|
Public sector1 |
(Percent of GDP) |
||||
|
General government |
|||||
|
Net lending/borrowing (overall balance) |
-3.4 |
-3.6 |
-1.5 |
2.2 |
2.9 |
|
Revenue |
31.8 |
32.7 |
33.3 |
36.2 |
35.3 |
|
Expenditures |
35.1 |
36.4 |
34.8 |
33.9 |
32.4 |
|
Primary balance |
-3.1 |
-3.2 |
-1.0 |
2.8 |
3.4 |
|
Nonoil balance |
-11.3 |
-9.7 |
-8.7 |
-8.4 |
-6.8 |
|
Federal government |
|||||
|
Net lending/borrowing (overall balance) |
-2.3 |
-3.4 |
-1.4 |
2.4 |
3.0 |
|
Nonoil balance |
-9.5 |
-9.0 |
-8.0 |
-7.2 |
-6.0 |
|
(Annual percent change) |
|||||
|
Base money |
-4.3 |
3.8 |
8.6 |
7.3 |
6.3 |
|
Ruble broad money |
11.3 |
9.2 |
10.5 |
7.5 |
6.5 |
|
External sector |
|||||
|
Export volumes |
6.4 |
2.6 |
7.8 |
1.3 |
2.2 |
|
Oil |
7.0 |
-1.2 |
-2.5 |
0.0 |
0.5 |
|
Gas |
6.5 |
7.1 |
5.8 |
4.0 |
1.0 |
|
Non-energy |
-8.0 |
-3.2 |
8.5 |
2.1 |
4.5 |
|
Import volumes |
-25.2 |
1.5 |
11.4 |
5.0 |
1.8 |
|
(Billions of U.S. dollars; unless otherwise indicated) |
|||||
|
External sector |
|||||
|
Total merchandise exports, fob |
341.4 |
281.8 |
353.0 |
435.7 |
442.0 |
|
Total merchandise imports, fob |
-193.0 |
-191.6 191.6 |
-238.0 |
-256.1 |
-263.9 |
|
External current account |
67.7 |
24.4 |
35.2 |
99.6 |
96.9 |
|
External current account (in percent of GDP) |
4.9 |
1.9 |
2.2 |
6.1 |
5.7 |
|
Gross international reserves |
|||||
|
Billions of U.S. dollars |
368.4 |
377.7 |
432.7 |
498.3 |
559.8 |
|
Months of imports2 |
15.7 |
17.0 |
15.9 |
17.0 |
18.5 |
|
Percent of short-term debt |
441 |
423 |
434 |
512 |
565 |
|
Memorandum items: |
|||||
|
Nominal GDP (billions of U.S.D) |
1,368 |
1,285 |
1,578 |
1,641 |
1,702 |
|
Exchange rate (rubles per U.S.D., period average) |
60.9 |
67.1 |
58.3 |
… |
… |
|
World oil price (U.S.D. per barrel) |
50.8 |
42.8 |
52.8 |
70.2 |
69.0 |
|
Real effective exchange rate (average percent change) |
-17.4 |
-1.2 |
14.6 |
… |
… |
|
Sources: Russian authorities; and IMF staff estimates. 1/ Cash basis. 2/ In months of imports of goods and non-factor services. |
|||||
-----
Earlier:

2018, September, 7, 12:17:00
ФОНД НАЦИОНАЛЬНОГО БЛАГОСОСТОЯНИЯ РОССИИ: $75 794,9 МЛН.МИНФИН РОССИИ - По состоянию на 1 сентября 2018 г. объем ФНБ составил 5 160 278,0 млн. рублей, что эквивалентно 75 794,9 млн. долл. США. Совокупный доход от размещения средств Фонда в разрешенные финансовые активы в 2018 г. составил 31 618,9 млн. рублей, что эквивалентно 522,7 млн. долл. США. |

2018, September, 3, 15:25:00
ЦЕНА URALS: $ 69,73МИНФИН РОССИИ - Средняя цена нефти марки Urals по итогам января – августа 2018 года составила $ 69,73 за баррель. В 2017 году средняя цена на Urals в январе – августе составила $ 50,09 за баррель. Средняя цена на нефть марки Urals в августе 2018 года сложилась в размере $ 71,72 за баррель, что в 1,4 раза выше, чем в августе 2017 года ($51,02 за баррель). |

2018, September, 3, 15:05:00
UNIMPORTANT RUSSIA SANCTIONSFT - Higher energy prices and a weakened rouble saw second-quarter profits soar at three of Russia’s largest oil and gas groups, underlining a strong earnings season for the country’s energy industry that has weathered international sanctions to reap strong earnings. |

2018, August, 31, 11:30:00
РОССИЯ: БОЛЬШЕ УГЛЯМИНЭНЕРГО РОССИИ - Заместитель Министра отметил, что потребление угля в мире ежегодно растёт на 2-2,5%, увеличиваются и объёмы поставок из России. «За двадцатилетний период доля России на международном рынке выросла с 6% до 14%. В этом году мы ожидаем, что экспорт угля из России составит около 200 млн т, это рекордные показатели за всю историю», - отметил замминистра. |

2018, August, 29, 10:50:00
РОССИЯ - ГЛОБАЛЬНЫЙ ЭНЕРГЕТИЧЕСКИЙ ЛИДЕРМИНЭНЕРГО РОССИИ - Президент добавил, что по итогам 2017 года Россия подтвердила свой статус одного из лидеров глобального энергетического рынка: «Мы заняли первое место в мире по объему добычи нефти, второе – по добыче газа. Россия входит в число ведущих стран по объему выработки электроэнергии и добыче угля: по электроэнергии – на четвертом месте, по углю – шестое место в мире». По словам Владимира Путина, в прошлом году сумма инвестиций в отрасли выросла на 10 процентов и составила 3,5 триллиона рублей. |

2018, August, 6, 13:35:00
ДОХОДЫ РОССИИ: + 388,3 МЛРД.РУБ.МИНФИН РОССИИ - Ожидаемый объем дополнительных нефтегазовых доходов федерального бюджета, связанный с превышением фактически сложившейся цены на нефть над базовым уровнем, прогнозируется в августе 2018 года в размере +388,3 млрд руб. |

2018, August, 3, 09:40:00
ВВП РОССИИ ВЫРОС НА 1,8%МИНЭКОНОМРАЗВИТИЯ РОССИИ - По оценке Минэкономразвития России, ВВП во 2кв18 вырос на 1,8 % г/г. Положительный вклад в динамику ВВП в апрелеиюне внесло промышленное производство, профессиональные услуги и финансовая деятельность. Ускорению экономического роста по сравнению с 1кв18 способствовало улучшение ситуации в транспортной отрасли и торговле, а также восстановление динамики строительного сектора. Рост ВВП в целом за январь–июнь оценивается на уровне 1,7 % г/г.
|






