
NUCLEAR POWER NEEDS INVESTMENT
IAEA - Nuclear power's electricity generating capacity risks shrinking in the coming decades as ageing reactors are retired and the industry struggles with reduced competitiveness, according to a new IAEA report. The declining trend may set back global efforts to mitigate climate change, IAEA Director General Yukiya Amano said.
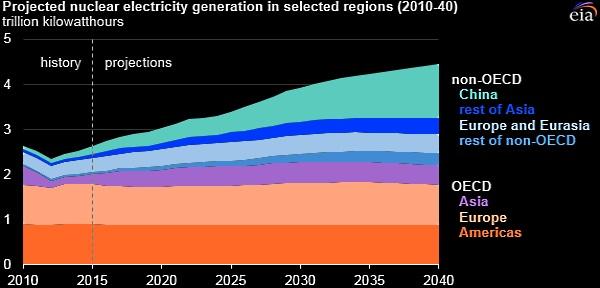
Overall, the new projections suggest that nuclear power may struggle to maintain its current place in the world's energy mix. In the low case to 2030, the projections show nuclear electricity generating capacity falling by more than 10% from a net installed capacity of 392 gigawatts (electrical) (GW(e)) at the end of 2017. In the high case, generating capacity increases 30% to 511 GW(e), a drop of 45 GW(e) from last year's projection. Longer term, generating capacity declines to 2040 in the low case before rebounding to 2030 levels by mid-century, when nuclear is seen providing 2.8% of global generating capacity compared with 5.7% today.
"The declining trend in our low projection for installed capacity up to 2050 suggests that, without significant progress on using the full potential of nuclear power, it will be difficult for the world to secure sufficient energy to achieve sustainable development and to mitigate climate change," Amano said.
The wide range in the projections is also due to the considerable number of reactors scheduled to be retired around 2030 and beyond, particularly in North America and Europe, and whether they will be replaced by new nuclear capacity.
Nuclear power produced about 10% of the world's electricity in 2017, accounting for about one-third of total low-carbon electricity. As of today, the world's 455 operating nuclear power reactors have a record level of 399.8 GW(e) total net installed capacity.
Over the short term, the low price of natural gas, the impact of renewable energy sources on electricity prices, and national nuclear policies in several countries following the accident at Japan's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in 2011 are expected to continue weighing on nuclear power's growth prospects, according to the report. In addition, the nuclear power industry faces increased construction times and costs due to heightened safety requirements, challenges in deploying advanced technologies and other factors.
Still, interest in nuclear power remains strong in the developing world, particularly in Asia where countries such as China and India need huge amounts of electricity and also want to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Commitments agreed to at the 21st session of the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP21) could also produce a positive impact on nuclear energy development in the future, according to the publication.
Regional Trends
Northern America: Nuclear electricity capacity could decrease by almost one-third in 2030 in the low case or maintain output near 2017 levels in the high case.
Latin America & the Caribbean: Nuclear electricity generating capacity is projected to increase in both low and high cases, but its role will remain small in the coming decades.
Northern, Western and Southern Europe: Several countries in these regions have announced a gradual phase-out of nuclear power. Generating capacity is projected to fall by as much as 30% or slightly increase by 2030.
Eastern Europe: Generating capacity is projected to maintain current levels or expand by 30% in the next two decades.
Africa: In the low case, generating capacity is projected to remain at current low levels, with the possibility of greater expansion by 2050.
Western Asia: Generating capacity is expected to increase significantly in the low and high cases.
Southern Asia: Generating capacity is projected to continue to grow in both the low and high cases.
Central and Eastern Asia: Nuclear electrical generating capacity is projected to increase significantly in both low and high cases.
-----
Earlier:

2018, September, 10, 12:20:00
ELECTRICITY & NUCLEAR OPPORTUNITIESWNN - The electrification of transport could potentially offer many opportunities for nuclear generation, Brandon Munro told the World Nuclear Association Symposium 2018 in London.
|

2018, August, 17, 11:50:00
GLOBAL NUCLEAR POWER UPWNA - Nuclear reactors generated a total of 2506 TWh of electricity in 2017, up from 2477 TWh in 2016. This is the fifth successive year that nuclear generation has risen, with output 160 TWh higher than in 2012. |

2018, July, 23, 13:25:00
GLOBAL ENERGY INVESTMENT DOWN 2%IEA - For the third consecutive year, global energy investment declined, to USD 1.8 trillion (United States dollars) in 2017 – a fall of 2% in real terms. The power generation sector accounted for most of this decline, due to fewer additions of coal, hydro and nuclear power capacity, which more than offset increased investment in solar photovoltaics. |

2018, July, 6, 11:40:00
RUSSIA'S ROSATOM: 67%ROSATOM - ROSATOM plans shortly to conclude contracts with new countries for construction of NPPs abroad. At the present time, ROSATOM has 67% of the world nuclear plant construction market, as head of the state-owned corporation Alexei Likhachev reported to Russia’s Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev. |

2018, July, 4, 12:05:00
THE FUTURE OF NUCLEAR POWERIEA - “Nuclear power is continuing to play an important role in electricity security along with other conventional generating technologies,” said IEA Executive Director Dr Fatih Birol in his opening remarks. “Despite this, with current policies there is little prospect for significant growth for nuclear power in developed economies on the horizon – although there are new efforts to spur innovations that could change this picture.” |

2018, June, 29, 10:30:00
URANIUM IS IMPORTANTWNN - For the foreseeable future, most new nuclear power technologies will still run, wholly or partially, on uranium, so it is important that this vital resource is mined, produced and managed sustainably, International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Director General Yukiya Amano said this week. It is also essential to take full account of environmental concerns, "both to ensure public acceptance today and to avoid troubling legacy issues in the future", he added. |

2018, May, 16, 11:45:00
GLOBAL NUCLEAR ENERGYWNN - Speaking on the opening day of the conference being held this week in Sochi, Russia, Rising said nuclear energy had a vital role to play in the global energy mix, providing a strong foundation of reliable and low-carbon generation to help support more variable clean energy generation options. |












