2050: RENEWABLES WILL BE HALF
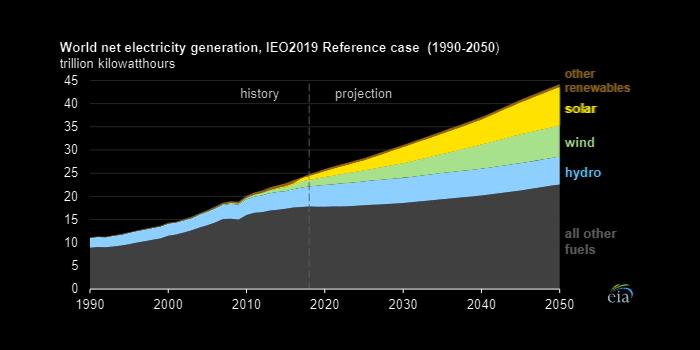
U.S. EIA - In 2018, 28% of global electricity was generated from renewable energy sources, most (96%) of which was produced from hydropower, wind, and solar technologies. In its International Energy Outlook 2019 (IEO2019), the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) projects that renewables will collectively increase to 49% of global electricity generation by 2050. Of the top three renewable sources, EIA expects solar's share of generation to grow the fastest and hydroelectric's share to grow the slowest.
EIA's international outlook includes analysis of eight countries and eight multicountry regions. Different regional- and technology-specific factors influence the growth rates of renewable technologies throughout the world.
Resource availability, renewable policies, regional load growth, and declining technology costs drive EIA's projected increase in global electricity generation from solar technologies. As more solar power systems have been installed, installation costs have experienced the steepest cost declines of all renewable technologies in recent years, and EIA expects that they will continue to decline as a result of learning-by-doing effects.
In many regions, solar resources are also generally more abundant than wind resources and typically follow very predictable daily and seasonal generation patterns. Resource availability and predictability and relatively simple plant construction technology also support favorable economics for solar photovoltaics, the most common solar generation technology in the IEO2019 Reference case.
EIA projects that China is the country that will see the most growth in solar generation because of its growing demand for electricity, favorable government policies, and competitive technology costs. Growth in solar generation is also strong in India, European countries in the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), and the United States—each of which have near-term renewable policies in place. IEO2019 Reference case projections for the United States are consistent with those in the Annual Energy Outlook 2019 Reference case.
Wind power is still a relatively new technology, and the declining capital costs it experiences as a result of learning-by-doing effects are not as steep as solar technologies. Wind technology adoption has significant growth potential, however, because many wind resource areas around the world are not yet developed.
Similar to solar power, EIA forecasts that near-term renewable policies in India and OECD Europe will lead to wind generation growth in those areas. In China, wind is among the many sources meeting the country's increasing demand for electricity.
Hydroelectricity was the predominant global renewable electricity generation source in 2018, but EIA expects relatively little growth in hydroelectric generation through 2050. Hydroelectricity is a mature technology, established in the nineteenth century, so many of the best sites for hydropower plants have already been developed. New hydro plants are not being built as rapidly as other renewable technologies because construction of new hydroelectric plants is relatively disruptive and capital intensive. The regions that EIA forecasts will have the greatest growth in hydroelectric generation in 2050 are areas such as China, Brazil, and OECD Europe, which tend to have extensive and accessible hydropower resources.
-----
Earlier: