IMPORTANT NUCLEAR ENERGY

НОВАТЭК - Москва, 24 июля 2019 года. ПAO «НОВАТЭК» сегодня опубликовало консолидированную промежуточную сокращенную финансовую отчетность по состоянию на и за три и шесть месяцев, закончившихся 30 июня 2019 г., подготовленную в соответствии с Международными стандартами финансовой отчетности (МСФО).
Основные финансовые показатели деятельности по МСФО
(в миллионах российских рублей, если не указано иное)
|
II кв.
2019 г.
|
II кв.
2018 г.
|
|
1П
2019 г.
|
1П
2018 г.
|
|
215 789
|
194 818
|
Выручка от реализации нефти и газа
|
446 973
|
373 303
|
|
2 724
|
1 004
|
Прочая выручка
|
5 646
|
1 922
|
|
218 513
|
195 822
|
Итого выручка от реализации
|
452 619
|
375 225
|
|
(157 507)
|
(135 606)
|
Операционные расходы
|
(332 647)
|
(266 643)
|
|
-
|
-
|
Прибыль от выбытия долей владения в дочерних
обществах и совместных предприятиях, нетто
|
308 578
|
1 645
|
|
(247)
|
(621)
|
Прочие операционные
прибыли (убытки), нетто
|
(1 161)
|
(519)
|
|
60 759
|
59 595
|
Прибыль от операционной деятельности нормализованная*
|
118 811
|
108 063
|
|
69 193
|
68 958
|
EBITDA дочерних обществнормализованная*
|
134 917
|
125 379
|
|
115 835
|
101 339
|
EBITDA с учетом доли в EBITDA
совместных предприятий нормализованная*
|
233 777
|
177 645
|
|
(277)
|
7 380
|
Доходы (расходы) от финансовой деятельности
|
(6 298)
|
12 782
|
|
23 282
|
(18 215)
|
Доля в прибыли (убытке) совместных
предприятий за вычетом налога на прибыль
|
94 255
|
(17 052)
|
|
83 764
|
48 760
|
Прибыль до налога на прибыль
|
515 346
|
105 438
|
|
69 175
|
32 041
|
Прибыль, относящаяся к
акционерам ПАО «НОВАТЭК»
|
450 971
|
75 162
|
|
64 296
|
54 289
|
Прибыль, относящаяся к акционерам
ПАО «НОВАТЭК», нормализованная**
|
130 026
|
101 199
|
|
21,35
|
18,01
|
Прибыль на акцию нормализованная** (в руб.)
|
43,17
|
33,57
|
|
31 203
|
22 052
|
Денежные средства, использованные
на оплату капитальных вложений
|
73 679
|
31 764
|
* Без учета эффекта от выбытия долей владения в дочерних обществах и совместных предприятиях.
** Без учета эффектов от выбытия долей владения в дочерних обществах исовместных предприятиях и от курсовых разниц.
Выручка от реализации и EBITDA
Во втором квартале 2019 года наша выручка от реализации составила 218,5 млрд руб., а нормализованный показатель EBITDA с учетом доли в EBITDA совместных предприятий составил 115,8 млрд руб., что представляет собой увеличение на 11,6% и 14,3% соответственно по сравнению с аналогичным периодом 2018 года. За шесть месяцев, закончившихся 30 июня 2019 г., наша выручка от реализации и нормализованный показатель EBITDA с учетом доли в EBITDA совместных предприятий составили 452,6 млрд руб. и 233,8 млрд руб., увеличившись на 20,6% и 31,6% соответственно по сравнению с отчетным периодом прошлого года.
Рост выручки и нормализованного показателя EBITDA в основном связан с запуском производства СПГ на второй и третьей очередях завода «Ямала СПГ» во втором полугодии 2018 года.
Прибыль, относящаяся к акционерам ПАО «НОВАТЭК»
Прибыль, относящаяся к акционерам ПАО «НОВАТЭК», выросла до 69,2 млрд руб. (22,97 руб. на акцию), или на 115,9%, во втором квартале 2019 года и до 451,0 млрд руб. (149,73 руб. на акцию), или в шесть раз, в первом полугодии 2019 года по сравнению с аналогичными периодами 2018 года. На прибыль Группы значительное влияние оказало признание в марте 2019 года прибыли от продажи 10%-ной доли участия в проекте «Арктик СПГ 2» в размере 308,6 млрд руб., а также признание в обоих отчетных периодах неденежных курсовых разниц по займам Группы и совместных предприятий, номинированным в иностранной валюте.
Без учета эффекта от выбытия долей владения в дочерних обществах и совместных предприятиях и эффекта от курсовых разниц, нормализованная прибыль, относящаяся к акционерам ПАО «НОВАТЭК», составила 64,3 млрд руб. (21,35 руб. на акцию) во втором квартале 2019 года и 130,0 млрд руб. (43,17 руб. на акцию) в первом полугодии 2019 года, увеличившись на 18,4% и 28,5% соответственно по сравнению с аналогичными периодами 2018 года.
Капитальные вложения
Денежные средства, использованные на оплату капитальных вложений, увеличились до 31,2 млрд руб., или на 41,5%, во втором квартале 2019 года и до 73,7 млрд руб., или на 132,0%, в первом полугодии 2019 года по сравнению с аналогичными периодами прошлого года. Значительная часть наших инвестиций в основные средства была направлена на развитие СПГ-проектов (проекта «Арктик СПГ 2» до марта 2019 года и проекта по созданию центра по строительству крупнотоннажных морских сооружений в Мурманской области), освоение Северо-Русского месторождения и разработку нефтяных залежей Восточно-Таркосалинского и Ярудейского месторождений.
Объем добычи и покупки углеводородов
|
II кв.
2019 г.
|
II кв.
2018 г.
|
|
1П
2019 г.
|
1П
2018 г.
|
|
149,0
|
131,8
|
Совокупная добыча углеводородов,
млн баррелей нефтяного эквивалента (млн бнэ)
|
296,1
|
264,3
|
|
1,64
|
1,45
|
Совокупная добыча (млн бнэ в сутки)
|
1,64
|
1,46
|
|
18 910
|
16 418
|
Добыча природного газа с учетом доли в
добыче совместных предприятий (млн куб. м)
|
37 570
|
32 926
|
|
9 935
|
10 562
|
Добыча природного газа в дочерних обществах
|
20 034
|
20 925
|
|
7 909
|
4 420
|
Покупка природного газа
у совместных предприятий
|
16 830
|
12 007
|
|
1 971
|
1 708
|
Прочие покупки природного газа
|
4 190
|
3 437
|
|
19 815
|
16 690
|
Итого добыча природного газа дочерних обществ и покупка (млн куб. м)
|
41 054
|
36 369
|
|
3 035
|
2 928
|
Добыча жидких углеводородов с учетом доли в добыче совместных предприятий (тыс. тонн)
|
6 022
|
5 864
|
|
1 607
|
1 650
|
Добыча жидких углеводородов
в дочерних обществах
|
3 207
|
3 278
|
|
2 366
|
2 322
|
Покупка жидких углеводородов
у совместных предприятий
|
4 679
|
4 622
|
|
51
|
56
|
Прочие покупки жидких углеводородов
|
107
|
100
|
|
4 024
|
4 028
|
Итого добыча жидких углеводородов дочерних обществ и покупка (тыс. тонн)
|
7 993
|
8 000
|
Объем добычи природного газа с учетом нашей доли в добыче совместных предприятий во втором квартале и в первом полугодии 2019 года вырос на 15,2% и 14,1% соответственно, а объем добычи жидких углеводородов увеличился на 3,7% и 2,7% соответственно по сравнению с аналогичными периодами 2018 года. Основным фактором, оказавшим положительное влияние на рост добычи, стал запуск производства СПГ на второй и третьей очередях завода «Ямала СПГ» во второй половине 2018 года.
Объем реализации углеводородов
|
II кв.
2019 г.
|
II кв.
2018 г.
|
|
1П
2019 г.
|
1П
2018 г.
|
|
18 764
|
15 149
|
Природный газ (млн куб. м)
|
40 959
|
35 412
|
|
|
|
в том числе:
|
|
|
|
15 114
|
14 496
|
Реализация в Российской Федерации
|
33 888
|
33 801
|
|
3 650
|
653
|
Реализация на международных рынках
|
7 071
|
1 611
|
|
4 130
|
4 273
|
Жидкие углеводороды (тыс. тонн)
|
8 106
|
8 050
|
|
|
|
в том числе:
|
|
|
|
1 841
|
2 028
|
Продукты переработки стабильного
газового конденсата
|
3 638
|
3 594
|
|
1 214
|
1 148
|
Сырая нефть
|
2 341
|
2 271
|
|
674
|
658
|
Сжиженный углеводородный газ
|
1 351
|
1 307
|
|
396
|
436
|
Стабильный газовый конденсат
|
768
|
872
|
|
5
|
3
|
Прочие нефтепродукты
|
8
|
6
|
Во втором квартале и в первом полугодии 2019 года объем реализации природного газа составил 18,8 млрд и 41,0 млрд куб. м, увеличившись на 23,9% и 15,7% соответственно по сравнению с аналогичными периодами 2018 года, в результате роста объемов реализации СПГ, приобретаемого у наших совместных предприятий OАO «Ямал СПГ» и OOO «Криогаз-Высоцк». По состоянию на 30 июня 2019 г. наши остатки природного газа составили 1,4 млрд куб. м по сравнению с 1,3 млрд куб. м на 30 июня 2018 г. и в основном относились к остаткам природного газа в подземных хранилищах. Остатки природного газа формируются в зависимости от потребности Группы в отборе природного газа для реализации в последующих периодах.
Во втором квартале 2019 года объем реализации жидких углеводородов уменьшился на 3,3% до 4,1 млн тонн по сравнению с 4,3 млн тонн в аналогичном периоде прошлого года главным образом за счет изменения остатков. При этом объем реализации жидких углеводородов в первом полугодии 2019 года по сравнению с первым полугодием 2018 года незначительно увеличился на 0,7%. По состоянию на 30 июня 2019 г. совокупный объем жидких углеводородов, отраженный как «Остатки готовой продукции и товары в пути», составил 852 тыс. тонн по сравнению с 806 тыс. тонн по состоянию на 30 июня 2018 г. Остатки наших жидких углеводородов изменяются от периода к периоду и, как правило, реализуются в следующем отчетном периоде.
Выборочные статьи консолидированного отчета
о финансовом положении (в миллионах рублей)
|
|
30.06.2019 г.
|
31.12.2018 г.
|
|
Активы
|
|
|
|
Долгосрочные активы
|
1 229 888
|
923 050
|
|
в т.ч. основные средства
|
455 605
|
408 201
|
|
в т.ч. инвестиции в совместные предприятия
|
451 844
|
244 500
|
|
в т.ч. долгосрочные займы выданные
и дебиторская задолженность
|
256 555
|
232 922
|
|
Текущие активы
|
381 807
|
293 320
|
|
Итого активы
|
1 611 695
|
1 216 370
|
|
ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬСТВА И КАПИТАЛ
|
|
|
|
Долгосрочные обязательства
|
219 905
|
222 752
|
|
в т.ч. долгосрочные заемные средства
|
144 777
|
170 043
|
|
Текущие обязательства
|
109 675
|
107 023
|
|
Итого обязательства
|
329 580
|
329 775
|
|
Итого капитал, относящийся
к акционерам ПАО «НОВАТЭК»
|
1 264 340
|
868 254
|
|
Доля неконтролирующих
акционеров дочерних обществ
|
17 775
|
18 341
|
|
Итого капитал
|
1 282 115
|
886 595
|
|
Итого обязательства и капитал
|
1 611 695
|
1 216 370
|
-----
IMPORTANT NUCLEAR ENERGY

WNN - 09 October 2019 - Nuclear power is "irreplaceable" and international cooperation in the technology "indispensible" in reducing global CO2 emissions, China National Nuclear Corporation (CNNC) President Jun Gu told delegates at the International Atomic Energy Agency's International Conference on Climate Change and the Role of Nuclear Power yesterday in Vienna. Climate change may in fact be an "opportunity to create a new era for nuclear energy", he said, and CNNC is "willing to work with all countries" to bring about a clean energy transition and mitigate climate change.
Of the 449 reactor units in operation in 30 countries today, 47 are in China, he noted. At nearly 50 GWe, they place the country in third ranking in terms of installed nuclear generating capacity. China also has 11 units under construction with an installed capacity of about 12 GWe, ranking the country first in the world in that respect, he said. In 2018, nuclear power generated 287 TWh of electricity in China, accounting for 4.2% of national power generation, and Gu is "fully confident" that China will add a further 6-8 units each year over the next 10 years.
"With technological progress, the world is entering an age of clean energy with less dependence on fossil fuel," Gu said. "The shares of natural gas, nuclear energy, solar power, wind power and hydropower in energy production and in consumption are increasing markedly. In some countries, clean energy takes about 60% of the energy mix. However, we think that hydropower is highly restricted by regional resources, and wind and solar power also have natural constraints. They can hardly be the main power producers without a breakthrough in energy storage technology. Also, nuclear power has been demonstrated as an important option in replacing coal-fired power plants on a large scale. Nuclear power is an important baseload option to avoid price fluctuation and the grid risk from renewable energy."
China is committed to cutting its CO2 emissions per unit of GDP by 60-65% from the 2005 level by 2030, he said, and plans to increase the share of non-fossil fuel energy in its primary energy mix to 15% by 2020 and to 20% by 2030.
Since Chinese President Xi Jinping launched the country's new energy policy in 2014, "tremendous changes" have been made, Gu said. "The past three years have witnessed the fastest growth of renewable energy in China, which now ranks first in installed capacity of hydro, wind and solar power, as well as in nuclear power construction."
The country's international cooperation in nuclear power is clear, he said, since it has reactor designs that include French PWRs, Canadian Candus, Russian VVERs and US AP1000s. It is also working on its own design, the HPR-1000, and is developing indigenous equipment supply.
"We have developed the capacity to manufacture equipment for eight to 10 units every year," he said. "At present, more than 85% of the key equipment and materials of our own HPR-1000 can be produced in China."
The HPR-1000, also known as Hualong One, is a Chinese pressurised water reactor design developed by CNNC and the China General Nuclear Power Group. The first HPR-1000 units to be constructed will be Fuqing units 5 and 6, followed by Fangjiashan units 3 and 4, and Fangchenggang units 3 and 4. There are five Hualong One reactors planned for Pakistan - four at Karachi and one at Chashma, of which two are under construction at Karachi. Construction of another HPR-1000 is planned to start next year in Argentina.
The HPR-1000 project is "progressing smoothly", Gu said, adding that Fuqing 5 had entered the commissioning stage and would achieve power operation by the first-half of next year.
CNNC is working on new nuclear technologies, he said, including small modular reactors, nuclear waste transmutation and treatment, accident-tolerant fuel, high-temperature reactors, fast breeder reactors, nuclear fusion technology, and used fuel disposal.
In July, CNNC announced the launch of a project to construct an ACP100 small modular reactor at Changjiang in Hainan province. Construction of the demonstration unit - also referred to as the Linglong One design - is scheduled to begin by the end of this year.
Its HTR-PM, a 200-megawatt high-temperature gas-cooled reactor, can supply industrial heat of above 750 degrees Celsius, he said, and is expected to have "broader prospects" in hydrogen production. The unit will be in operation by the end of next year, "laying a solid foundation for further commercial application", he added. In addition, CNNC has developed the Yanlong DHR-400 pool-type low-temperature reactor in northern China to replace the fossil fuel-fired district heating system. The company is also working with 'Belt-and-Road countries' in nuclear power, uranium resources, nuclear fuel, and the non-power applications of nuclear technology. And it is engaged in the ITER fusion project in the south of France.
International cooperation, he said, can "build consensus and strengthen confidence" in nuclear power.
"The global nuclear industry is moving out of the shadow of Fukushima accident. However some countries have abandoned nuclear power and sharply dropped its proportion in their generation mix," he said. "Developed countries have witnessed sluggish growth of nuclear power - except for six units in Finland, France, the US and the UK, no other nuclear power plant had been built in North America and the EU area for about 30 years. Over the same period however about 100 units were built in developing and emerging economies."
-----
Earlier:
2019, October, 9, 13:10:00
THE NEW NUCLEAR POWER INVESTMENTS
"Greater magnitudes of uncertainty lead to volatility," he said, "and for a capital-intensive sector like ours, this means less investment and more risk to security of supply. This is especially true in power markets that are open to competition: their market design must be adaptive, and long-term contracts used for all types of generation."

2019, October, 8, 12:55:00
NUCLEAR ENERGY SUSTAINABILITY
How can the IAEA help make sure that nuclear energy is sustainable?
A short animation detailing the IAEA's International Project on Innovative Nuclear Reactors and Fuel Cycles (INPRO).

2019, October, 7, 13:05:00
THE GLOBAL NUCLEAR TECHNOLOGIES
"The global nuclear industry today is becoming a factory of new technologies. These are IT-technology, supercomputers and new materials. These are nuclear medicine and new types of power generation, including wind energy. We not only see the modern agenda and participate in it, we form this agenda. And new technologies are what makes people's lives better, more comfortable and safer," Likhachov said.
2019, October, 2, 11:45:00
NUCLEAR POWER - 2050: UPDOWN
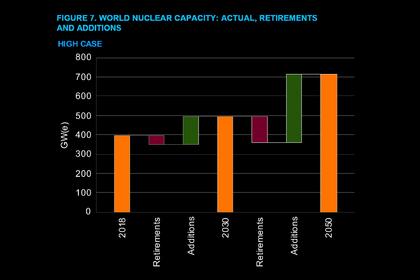
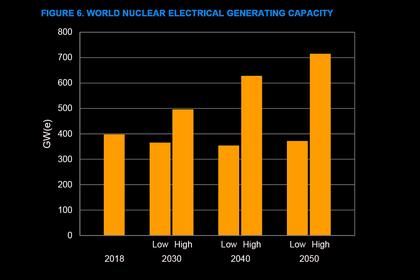
The new projections to 2030 see generating capacity declining by some 8% in the low case and increasing by 25% in the high estimate. By 2050, it’s seen falling by 6% in the low scenario and rising by 80% in the high case. Compared with last year, the new estimates to 2050 are down by 33 GW(e) in the high case and up by 15 GW(e) in the low case.

2019, September, 30, 15:10:00
ENERGY CHANGES CLIMATE
These three levers, each with their own potential to disrupt the market and offer new growth opportunities to the companies that leverage them, are often discussed in the energy industry: Digital technology, climate change, and dealing with risk
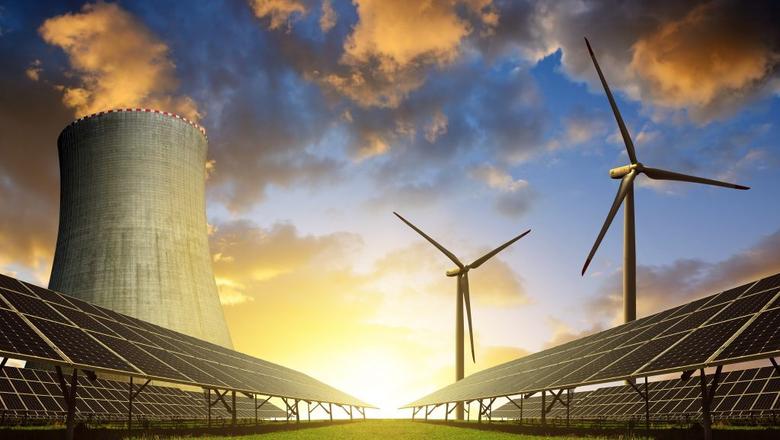
2019, September, 26, 13:25:00
CLEAN NUCLEAR POWER
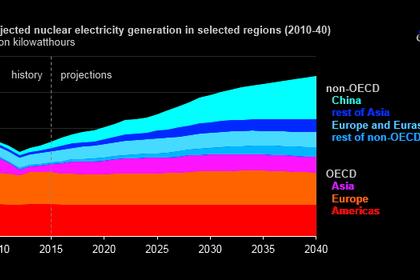
Nuclear reactors are the unsung heroes as we set out to respond to the climate change challenge. The need for nuclear energy has never been greater - there simply is no other energy source which can deliver deep decarbonisation within the necessary timeframes.
All Publications »
Tags:
NUCLEAR,
ENERGY,
POWER,
CLIMATE













