U.S. FINANCIAL STABILITY: NOV 2019
U.S. FRB - Financial Stability Report, November, 2019
Overview
This report reviews conditions affecting the stability of the financial system by analyzing vulner abilities related to valuation pressures, borrowing by businesses and households, financial leverage, and funding risk It also highlights several near-term risks that, if realized, could interact with such vulnerabilities.
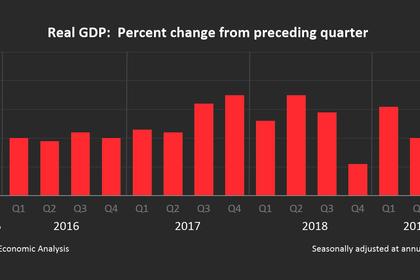
Investor appetite for risk generally appears to have returned to a level in the middle of its historical range but remains elevated for some important classes of assets Debt loads of businesses are historically high The core of the financial sector appears resilient, with leverage low and funding risk limited relative to the levels of recent decades Overall, the level of vulnerabilities in the financial system has moved little since the publication of the Board’s Financial Stability Report in May 2019
Our view on the current level of vulnerabilities is as follows:
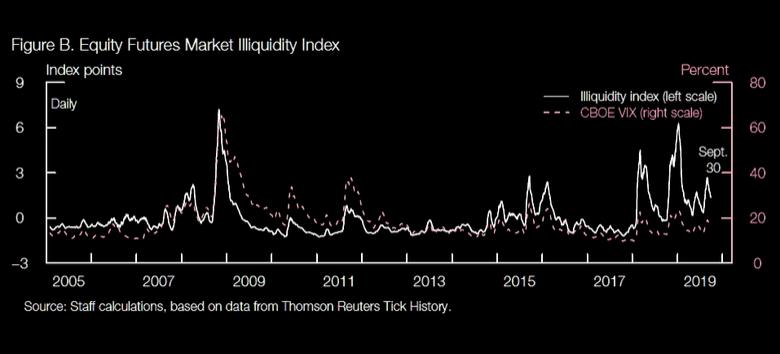
• Asset valuations. Asset prices remain high in several markets relative to income streams However, risk appetite measures that account for the low level of long-term yields on US Treasury securities are more aligned with historical norms for most markets With the exception of riskier corporate debt, commercial real estate (CRE), and farmland markets, these measures point to a reduction in risk appetite from the elevated levels of 2017 and 2018.
• Borrowing by businesses and households. Borrowing by businesses is historically high relative to gross domestic product (GDP), with the most rapid increases in debt concentrated among the riskiest firms amid weak credit standards By contrast, household borrowing remains at a modest level relative to income, and the amount of debt owed by borrowers with credit scores below prime has remained flat.
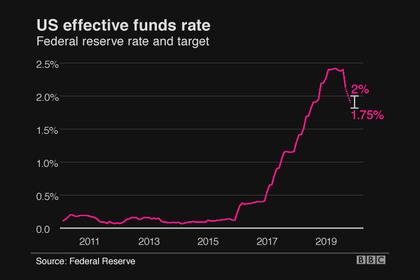
• Leverage in the financial sector. The largest U S banks remain strongly capitalized, and the leverage of broker-dealers is at historically low levels However, several large banks have announced plans to reduce their voluntary capital buffers Leverage among life insurance companies is moderate, while hedge fund leverage remains elevated relative to the past five years.
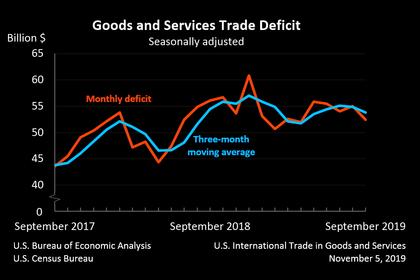
• Funding risk. Estimates of the total amount of financial system liabilities that are most vulnerable to runs, including those issued by nonbanks, remain modest Short-term wholesale funding continues to be low compared with other liabilities, and the ratio of high-quality liquid assets to total assets remains high at large banks Stresses in Europe, such as those related to Brexit; stresses in emerging markets; and an unexpected and marked slowdown in U S economic growth are among the near-term risks that have the potential to interact with these vulnerabilities and pose risks to the financial system.
-----
Earlier: