U.S. SOLAR POWER UP
PLATTS - Data released Thursday in the Solar Energy Industries Association third-quarter 2019 market report shows a segment of the US power generation industry that is surging.
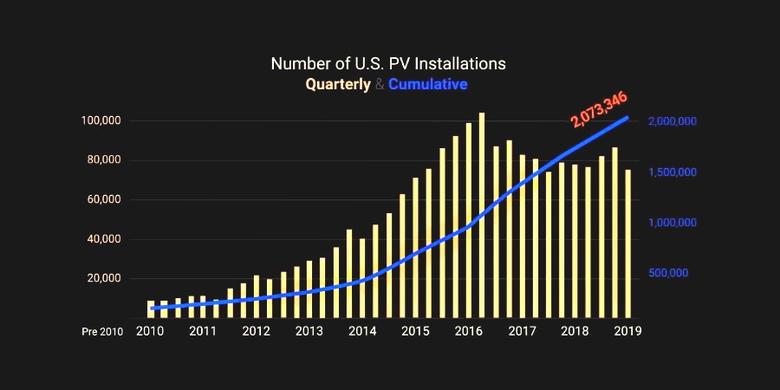
The SEIA said 2.6 GW of solar PV was installed in the third quarter of this year, which was a 25% increase from Q2 2019 and an increase of 45% from Q3 2018. In the past quarter, companies installed a "record-setting" 700 MW of residential rooftop PV.
The Washington-based solar association that works with Wood Mackenzie Power & Renewables in preparing its quarterly report said it believed total installed PV capacity in the US will "more than double" over the next five years, with annual installations reaching 20.1 GW (DC) in 2021, "prior to the expiration of the federal Investment Tax Credit for residential systems and a drop in the commercial credit to 10%."
At the same time, non-residential or C&I PV installations were flat on a quarterly basis and continue to see pipelines diminish due to policy "transitions and persistent interconnection issues in key commercial markets."
The report noted, however, that more than 1.4 GW of utility-scale installations came online in Q3, with new project procurement expanding the contracted pipeline to 45.5 GW.
Wood Mackenzie said in the report that it believes that for all of 2019, solar installations of all types will reach 13 GW, which would be a 23% year-over-year increase from 2018.
The report also said, "Across all market segments, solar PV accounted for 39% of all new electricity-generating capacity additions in 2019 through Q3."
LOW UTILITY-SCALE SOLAR PPA PRICES
The 1.4 GW of utility-scale solar capacity that came online in Q3 represented 55% of all the solar capacity additions made in the quarter.
Wood Mackenzie projects an additional 4.6 GW of utility PV capacity additions in just the fourth quarter of this year, which would bring the total of new utility-scale capacity to 8 GW for all of 2019.
The SEIA said there are 10.4 GW of utility-scale solar projects under construction, with the contracted pipeline of projects standing at 45.5 GW, "the highest it has ever been in the history of U.S. utility-scale solar."
"The massive growth of new projects continues to be spurred by utilities and developers looking to safe-harbor enough equipment for as much capacity as possible under the 30% ITC," the report said.
It said it was "notable" that 5.4 GW of utility-scale solar projects have been announced in Texas.
"While most projects have utility or corporate off-takers, a growing portion of them are being built as merchant projects to sell power directly into the ERCOT market."
'AMBITIOUS' TARGETS
Overall demand for utility PV will remain robust through 2024 even after the current surge in procurement subsides.
The report points to the Tennessee Valley Authority, PacifiCorp, Duke Energy and Idaho Power as power generators that have released updated integrated resource plans that outline what the report calls "increasingly ambitious utility-scale solar procurement targets for dates both before and after the ITC step-down."
Also, the number of new and repeat corporate off-takers continues to rise, with 4.8 GWdc of new offsite C&I projects announced so far in 2019.
"Voluntary procurement of utility PV based on cost-competitiveness continues to be the primary driver of projects announced in 2019, accounting for 51% of the total. This procurement has been driven by the low cost of utility PV, with recently signed PPA prices ranging from $18 to $35/MWh.," the SEIA/Mackenzie report said.
-----
Earlier: