
IMPORTANT EUROPE'S NUCLEAR
WNN - Nuclear energy can help the European Union achieve a sustainable and low-carbon future while providing people with reliable and affordable electricity, Foratom - the European nuclear trade body - says in a new position paper.
In late November, the European Commission adopted a strategic long-term vision for a "prosperous, modern, competitive and climate neutral economy" by 2050. The strategy - referred to as A Clean Planet for All - shows how Europe can lead the way to climate neutrality by investing into "realistic technological solutions, empowering citizens, and aligning action in key areas such as industrial policy, finance, or research", according to the Commission. This transition can be made, it suggests, "while ensuring social fairness". Each of the eight possible scenarios for the European Union includes a significant share of electricity generated by nuclear power.
In a new position paper, Foratom highlights nuclear energy's three main advantages in the context of meeting the EU's aim: environmental sustainability, energy independence and economic contribution.
"Based on the current climate change debate, it is important that nuclear energy capacity is maintained (and preferably increased) in order for the EU to achieve its target," Foratom said. "Nuclear energy will help the EU meet its 2050 objectives both in terms of ensuring security of supply and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
"In order to achieve a fully decarbonised electricity sector by 2050, the European Union needs an energy mix with at least one-quarter nuclear," it added. "This translates into a minimum of 150 GWe of installed nuclear capacity."
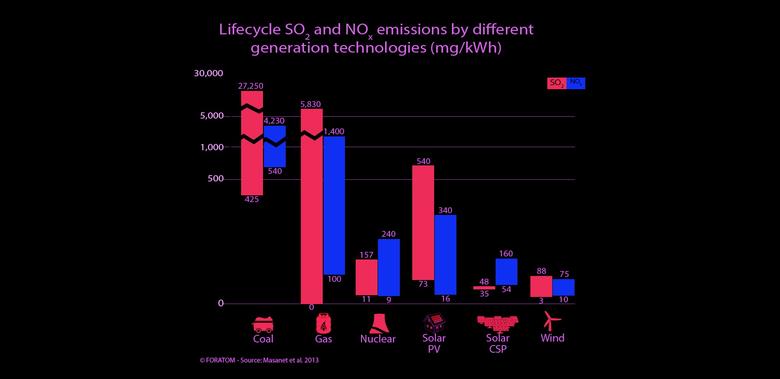
Foratom highlighted that, in addition to reducing carbon dioxide emissions, nuclear energy can limit other air pollutants, such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide. Nuclear power plants generate less waste compared with other energy sectors and also has significantly lower land requirements than other low-carbon energy sources.
Nuclear energy also increases the level of energy independence, "which is essential considering that the EU imports approximately half of the energy it consumes, with many EU member states dependent on one single external supplier," Foratom noted.
Nuclear energy is economically and socially sustainable, the organisation said. Nuclear electricity generation costs are much less affected by potential fuel price spikes as uranium costs are only a small component of the total cost of production.
"The nuclear industry also contributes significantly to the economic growth of the countries which chose it as it offers a large amount of long-term highly skilled jobs," Foratom said. It estimates the industry currently provides some 800,000 jobs in Europe.
"The recognition of nuclear energy by the European Commission as an essential element of Europe's low-carbon future is a step in the right direction", said Yves Desbazeille, Director General of Foratom. "It's important to keep in mind that nuclear energy is capable not only of reducing CO2 emissions, but also provides many other benefits as it ensures security of energy supply and is environmentally, economically and socially sustainable."
The 128 nuclear power reactors (with a combined capacity of 119 GWe) operating in 14 of the 28 EU member states currently account for over one-quarter of the electricity generated in the whole of the EU. Nuclear accounts for 53% of the EU's carbon-free electricity.
The global nuclear industry has set the Harmony goal for nuclear energy to provide 25% of global electricity by 2050. This will require trebling nuclear generation from its present level. Some 1000 GWe of new nuclear generating capacity will need to be constructed by then to achieve that goal.
-----
Earlier:

2019, January, 30, 10:40:00
FRANCE'S NUCLEAR CHANGESWNN - President Emmanuel Macron announced last November that a total of 14 French power reactors of 900 MWe capacity will be shut down in order to reduce the share of nuclear in the country's electricity generation mix from the current 75% to 50% by 2035. |

2019, January, 23, 10:55:00
GERMANY NEED COALPLATTS - The government-appointed coal commission is finalizing recommendations this week for the phase-out of coal-fired power stations, which provide 35% of Germany's generation mix. |

2018, December, 14, 08:55:00
GERMANY'S RENEWABLE: 38%PLATTS - Renewables' share in Germany's power mix is set to reach 38% this year, ahead of the government's 2020 target of 35% but below-trajectory for 2030's 65% target, utility lobby group BDEW said Thursday. |

2018, December, 12, 08:35:00
FRANCE'S NUCLEAR UP BY 8%REUTERS - Electricity production from French nuclear reactors rose 8 percent in November compared with the same month a year-ago due to a low volume of outages, state-controlled utility EDF said on Monday. |

2018, December, 10, 08:20:00
BRITAIN'S FUSION ENERGYWNN - The UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) and First Light Fusion are collaborating on a project to convert fusion reactions into heat to enable clean power production. The 'fusion island' project is to be partly funded by a grant from the Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy (BEIS). |

2018, November, 16, 09:00:00
FRANCE'S NUCLEAR POWER: 396 TWHPLATTS - French nuclear performance has improved following a near-record low 379 TWh in 2017, but this is still only the fourth time this century for annual output below 400 TWh for the current fleet of 58 reactors. |

2018, November, 12, 11:50:00
SMALL BRITAIN'S NUCLEARWNN - Advanced Nuclear Technologies - otherwise known as small nuclear or small reactor technologies - encompass a wide range of nuclear reactor technologies under development, BEIS noted. "The common attributes that these technologies share is that they are smaller than conventional nuclear power station reactors and are designed so that much of the plant can be fabricated in a factory environment and transported to site, reducing construction risk and making them less capital-intensive," it said. |












