EUROPE'S GAS DEMAND DOWN
PLATTS - 10 Jul 2020 - Gas consumption in the EU-27 dropped by 5% year on year in the first quarter to 130.8 Bcm, the latest quarterly market report published July 10 by the European Commission showed.
The fall in demand reverses the trend from the previous two quarters, which saw year-on-year gains of 7% and 2% respectively.
The market report excludes the UK -- which left the EU at the end of January -- in both absolute terms and for year-on-year comparisons.
"Weather across Europe was generally warmer in January-March 2020 compared to the seasonal average, resulting in less heating-related demand for gas in the residential sector," the EC said.
Gas demand for power generation was down 1.8% in Q1, it said. "The decrease in gas demand in the electricity generation sector was aggravated by the decreasing industrial demand induced by the COVID-19 lockdown measures in the last weeks of the quarter," it said.
Gas consumption in Q1 fell by more than 20% year on year in a number of EU countries, including Romania, Latvia, Finland and Slovakia.
But in absolute numbers, gas consumption in Q1 fell the most in Germany and Italy (both by 1.7 Bcm), Romania (1.3 Bcm), France (1.1 Bcm), Slovakia (0.4 Bcm), Spain (0.3 Bcm), and Finland (0.2 Bcm).
Gas demand actually rose in several countries, including Malta -- though from a very small base -- Portugal, Hungary, Croatia and the Netherlands.
EU production, imports
EU gas production dropped sharply by 23% year on year in Q1, amounting to just 16 Bcm.
The Netherlands produced 7.2 Bcm of gas, down from 10.6 Bcm in Q1 2019, followed by Romania (2.5 Bcm), Germany (1.3 Bcm) and Italy (1.1 Bcm).
"Beyond subdued gas demand, production in the Netherlands and other EU countries was also impacted by competitive LNG imports," the EC said.
EU net gas imports fell by 7% year on year in Q1, with Russian pipeline supplies covering 40% of extra-EU net gas imports.
LNG covered 28% of the total EU imports, while Norwegian pipeline gas was only the third biggest import source at 24%.
It was followed by pipeline imports from North Africa at 6%.
Net gas imports amounted to 81 Bcm in Q1 2020.
The five biggest importers in the EU in Q1 were Germany (24 Bcm), Italy (16 Bcm), France and Spain (both 8 Bcm) and Belgium (6 Bcm), representing together close to 80% of the total EU net gas imports in the quarter.
The EC said that after the UK left the EU in January, the gas import dependency of the EU-27 increased further.
In 2018 import dependency stood at 83.2% compared with 77.4% including the UK.
LNG supplies
In Q1 2020 the EU imported 25 Bcm of LNG, and the three biggest importer countries were: Spain (6 Bcm), France (5 Bcm) and Belgium (4 Bcm).
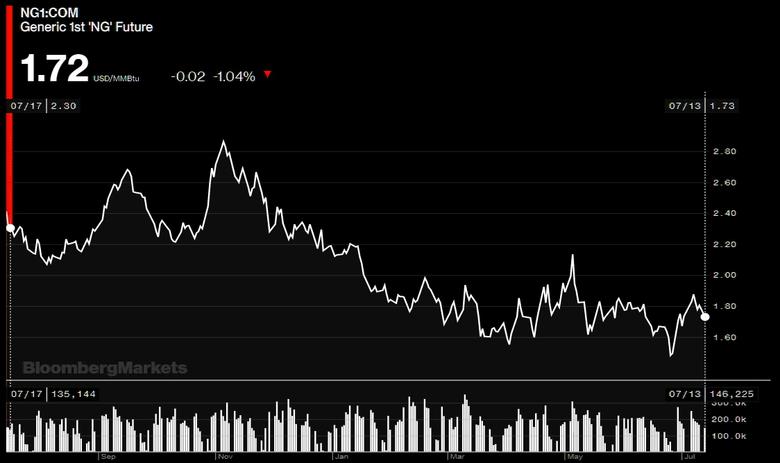
With low gas prices through Q1, the EU's estimated gas import bill fell to the lowest in the last six years, amounting to Eur9.8 billion ($11.1 billion) in the quarter.
That was down from Eur18.7 billion in Q1 2019.
The LNG import bill of the EU was estimated at Eur3.3 billion, down from Eur4.8 billion in the same period a year ago.
The EC said that "reflected the impact of falling LNG import prices, even if LNG imports grew in volume."
Q1 traded volume on European gas hubs rose 32% year on year to 5,010 TWh, "principally owing to increasing hedging activity on the markets as prices became more volatile and contract price differences widened," the EC said.
The share of trade on the Dutch TTF, the most liquid hub in the EU, was 74% among the observed European hubs.
-----
Earlier: