
P2P ENERGY TRADE
By Dr. Amal Khashab Expert Independent Consultant ,Electric Power Systems Engineering Self
ENERGYCENTRAL - Peer-to-Peer Distributed Energy Trading
Background
Traditionally, non-renewable energy sources such as coal, oil and natural gas are being depleted and becoming more expensive from time to time which indicates that the energy from these sources will not be able to support the increasing demand caused by a growing population. Moreover, non-renewable energy sources are not environmental friendly as they cause high level of carbon emissions. All these factors have motivated the emergence of various kinds of renewable energy sources (RES) such as solar panels and wind turbines.
Renewable Energy Sources (RES) utilization witnessed high penetration levels all over the world biased by the decreasing cost of installation based on their learning curves.
Also, micro grids of distributed Renewable Energy Sources witnessed a wide spectrum applications to avoid the cost of transmission networks.
Currently, excess intermittent solar and/or wind energy is exported back to the utility's grid for a small feed-in tariff rate. However, this method is becoming obsolete as more people are looking for flexibility and control in managing how their resources are distributed.
Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading Concept
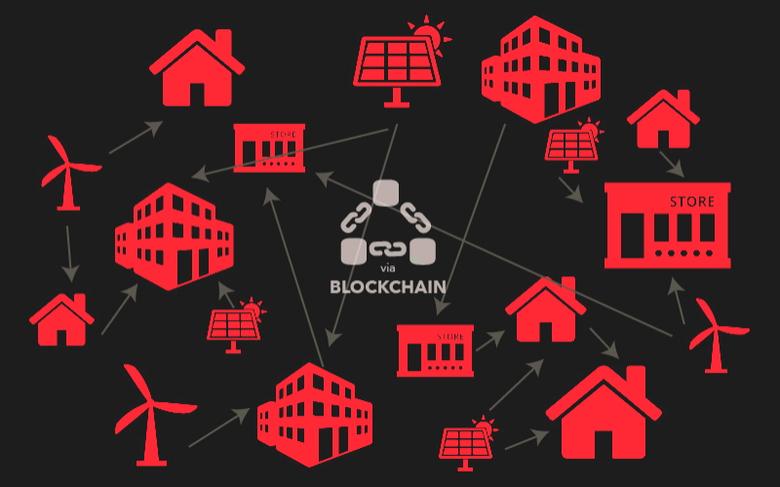
Peer-to-peer energy (P2P) trading is the buying and selling of energy between two or more grid-connected parties. Often in the form of solar energy, any excess energy can be transferred and sold to other users via a secure platform. Peer-to-peer energy trading allows consumers the choice to decide on whom they purchase electricity from, and who they sell it to.
The trading of energy is done through a secure platform, often using a technology like blockchain. Blockchain is a database technology that processes and stores information, such as transactions of assets. These assets can be in the form of renewable energy credits, which can be traded through the database. Peer-to-peer energy trading platforms such as blockchain will allow consumers to share their excess energy among one another and control how it’s distributed through micro-grids. Users who both sell and consume energy are called prosumers. Even if you don’t have solar panels, you can still purchase energy from others.
Peer -to-Peer Potential Benefits
Due to the expansion of distributed renewable energy resources, peer to peer energy trading is expected to be one of the key elements of next generation power systems. It can provide various benefits such as:
- Energy does not have to be transported from centrally located power plants, reducing electricity transportation costs (about 40% of electricity cost goes to maintain and manage the transmission and distribution networks to deliver electricity from generating stations to the customers premises)
-
Ability of buyers to access renewable energy at a reasonable price from neighbours, and ability for sellers to get a price more than they’d receive as a feed-in tariff from their retailer.
-
Providing a choice for dealing with other consumers and cutting out the middle man (electricity retailers).
-
Using blockchain, all transactions are public and once on the blockchain cannot be altered in any way creating full transparency.
Peer -to-Peer Related Issues
1. Maintaining the balance between supply and demand
It is an important criterion for the security and reliability of power systems. Mismatch between supply and demand may lead to system instability and failure. In Peer-to -Peer power is generated in a distributed manner and is controlled by several producers. Moreover, power generation is highly unpredictable as it depends on RES that are affected by weather conditions.
Therefore, achieving demand response optimization is more difficult as compared to existing systems. As a result, new methods of energy scheduling and price optimization algorithms based on game theory, collaboration, incentives and centrally controlled models have been proposed by several studies.
2. Power routing
This is a mechanism that allows energy routing between prosumers and consumers residing in different geographical locations.Moreover, power routing in distributed systems is more challenging due to integration problems as it might require power conversion from one form to another. Power routing has gained considerable attention from the research community. However, existing systems do not provide this functionality.
Practices of Peer to Peer Energy Trading
1. The first recorded peer-to-peer energy trade occurred in Brooklyn, New York, in 2016 when a resident with solar panels sold a few kilowatt hours to his neighbor via the Ethereum blockchain.
Since then, the idea has circulated the globe. While integration has been slow, mostly due to the current market, there have been several residential trials taking place in Australia and other parts of the world.
Here are just a few of the companies breaking ground in the peer-to-peer trade across the globe:
2. LO3
LO3 is revolutionizing the way energy is shared and distributed. Using a platform called Exergy, households and businesses trade electricity on an auction market. Following a huge success in New York with the Brooklyn Microgrid, LO3 is now working on a closed-market project in South Australia, partnering with Yates Electrical Service.
3. SonnenFlat
SonnenCommunity is an exclusive group made up of sonnenBatterie customers. Acting similar to a P2P trading platform, SonnenCommunity members are able share their excess solar energy to others through a program called sonnenFlat.
SonnenFlat customers must have a solar PV system of at least 5kW and a sonnenBatterie eco 8.8 or above to participate. The benefit of sonnenFlat means users can avoid unexpected price hikes and increased rates, and instead just pay a flat fee, with any excess energy charged accordingly.
4. Power Ledger
Power Ledger is an Australian technology company that has developed a blockchain-enabled peer-to-peer renewable energy trading platform. The platform facilitates the buying and selling of renewable-generated electricity in real time, enabling users with solar panels to trade their excess solar energy with their neighbors. The company has already formed partnerships with energy retailers, industry bodies and local governments to deploy the technology and currently has 22 projects across eight countries including Australia, the United States, Italy and Thailand.
Power Ledger’s technology won Sir Richard Branson’s global Extreme Tech Challenge award in 2018.
5. Grid+
Just like many peer-to-peer energy trading start-ups, Grid+ secured its capital through crowdfunding, raising $29 million before going live. The company, which operates in Texas, is hoping to pull in 100 million customers by the end of 2019.
Grid+ is owned by New York company, ConsenSys, which uses blockchain technology to create applications in many different fields.
6. Suncontract
Suncontract launched the world’s first trading platform on April 13th, 2018 in Slovenia. The company has partnered with European nations and many energy sectors and blockchain partnerships to provide an energy trading platform to households. Via an app, users can enter into deals with each other, set prices and share energy among one another. While the project is currently being implemented in Slovenia, it will shortly begin in the European Union where they have received support from the government and reputable EU commissioners.
7. Eemnes Energie
A partnership between Bax Company, Belgian tech provider Enervalis and Eemnes Energie has created the largest-scale peer-to-peer energy trading platform in Europe. The pilot project is based in the Netherlands, and will allow 4,000 participants the opportunity to sell and trade their renewable energy for the next 10 years. The companies are working together with the municipality of Eemnes, housing corporation De Alliantie, Chalmers University in Gothenburg (Sweden), the province of Utrecht, the Dutch Government and the European Union to establish and oversee the pilot.
While peer-to-peer energy trading may not be at the stage of mass integration just yet, the idea is quickly being adopted as a solution for the future. By revolutionizing this technology, consumers won’t need to rely on utility retailers for their energy, and can make smart, sustainable choices about how they use and distribute energy.
8.Toshiba explores peer-to-peer energy trading with Japanese utility
One year-long research, in which they will look at different models involving technologies such as solar power, battery storage and blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT).
However, detailed business models have yet to be established and it is unclear what impact an increase in these transactions will have on electrical distribution systems.
The two companies will work towards bolstering the efficiency of renewable energy usage while also building new business models that can grow the business domains of the future.
-----
This thought leadership article was originally shared with Energy Central's Grid Professionals Community Group. The communities are a place where professionals in the power industry can share, learn and connect in a collaborative environment. Join the Grid Professionals Community today and learn from others who work in the industry.
-----
Earlier:

2020, June, 15, 13:25:00
ENERGY TRADING: COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE
Once considered a bulwark against the forces of modernization, industry and technological change is pushing energy trading organizations to consider a number of strategic changes to their front, middle, and back office functions that optimally engage people and systems to navigate our VUCA world.
|

2020, June, 15, 13:20:00
ENERGY INDUSTRY: DATA MANAGEMENT
The energy value chain is very complex, from generation, to transmission, distribution, energy trading, and energy sales.
|

2020, January, 6, 10:43:00
BLOCKCHAIN-BASED ENERGY TRADING
a blockchain-based peer-to-peer energy trading system, has been approved to conduct a 12-month pilot program for energy trading
|












