BRITAIN'S NUCLEAR: CHEAPER
NUCLEAR ENGINEERING - 3 September 2020 - The UK Nuclear Industry Association (NIA) has launched a new report, in which a cross-industry team, working as part of the government-backed Nuclear Sector Deal, set out the key factors to reduce risk and bring down costs by 30% by 2030.
These factors include rigorous pre-construction planning, with simplicity of design and construction methodology, repeating designs across multiple stations, and building up and transferring a skilled and experienced workforce to new projects, NIA said.
The report also identified how a new financing model that controls construction risk will also bring down consumer costs by mobilising a wider pool of investors and cutting the cost of capital. It incorporates lessons from projects worldwide and argues that nuclear power is vital to achieving Net Zero by 2050, whilst creating jobs and economic opportunities across the UK.
Humphrey Cadoux-Hudson CBE, chair of the Cost Reduction Working Group of the Nuclear Sector Deal, said: “I am very pleased to say that the nuclear new build cost reduction workstream has made great progress, and our report clearly shows it’s possible to deliver a cost-effective programme of new nuclear power stations in the UK. But promises of cost reduction are not enough – in making this case, the developers of new nuclear plants are showing that we recognise the delivery risks we face, and how to manage them.”
NIA CEO Tom Greatrex said nuclear power stations are very cost effective to run due to "high reliability, low and predictable fuel costs and very large volumes of power generated whatever the weather."
"This report demonstrates that the upfront costs can be tackled effectively by bearing down on construction complexity and risks, and by tackling unnecessarily high financing costs,” he added.
To embed this framework, the industry is developing a comprehensive Risk Assessment Tool which will monitor 14 key factors for project delivery and efficiency, according to NIA. The tool will enable developers, investors and government to develop clear understanding of project risks to support investment decisions, and then track the ongoing management of those actions and risks throughout the delivery of the project.
The 14 factors that will be monitored are: financing, regulation, governance, site data, technology data, design, estimates, contractual interfaces, project management, data system, construction preparation, supply chain, skills and operations preparation.
NIA said the industry has achieved early progress against these initial indicators:
- Rigorous pre-construction planning: designs should be as mature as possible, and all key stakeholders aligned on the scope and scheduling of a project before construction begins. The designs that will be used at Wylfa Newydd and Sizewell C are highly advanced, and years of work have been undertaken to prepare the delivery organisations for construction.
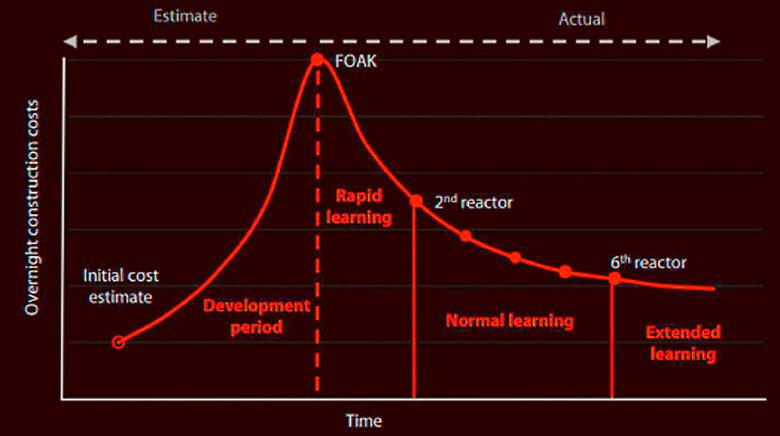
- Repeating designs: constructing a number of the same reactors dramatically reduces design costs, allows the application of best practice from previous projects and facilitates continuous investment in the supply chain and workforce training. Hinkley Point C has borne first generation costs for new nuclear in the UK, and setting up the supply chain, skilling workers, and building capabilities will reduce costs for all subsequent large-scale reactors. Wylfa Newydd will use the Advanced Boiling Water Reactor, which been built on time and budget four times in Japan between 1992 and 2006. The last station was built in just 37 months.
- Transferring skilled labour: workers can apply their learnings and experience from building one plant to building another. At Hinkley Point C, it took 16 hours to install a tonne of rebar at Unit Two, down from 25 hours for Unit One – a 36% reduction.
The industry is confident that by taking the steps outlined in the report, and by action from Government to secure a new financing model, costs will fall in accordance with the commitments made under the Nuclear Sector Deal.
-----
Earlier: