NUCLEAR ACHIEVE SDG GOALS

WNA - Nuclear’s contribution to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals
1. Nuclear generation helps reduce poverty and stimulates economic growth
Globally, more than 700 million people do not have access to electricity. Billions more have unreliable supplies. A reliable, clean and affordable electricity supply is essential to enable people to rise out of poverty and improve their quality of life. It is also a prerequisite for achieving many of the other UN Sustainable Development Goals.
Alleviating poverty also means providing people with well-paid jobs and supporting economic growth, particularly in developing countries. The construction and operation of nuclear plants provides such employment opportunities, as well as stimulating investment in infrastructure and education, and having a strong multiplier effect on national economies.
The impacts of poverty are particularly acute in the least developed countries, but fuel poverty can be experienced by low-income households in even the most developed countries.
Nuclear generation costs are much less susceptible to fuel price volatility than fossil fuel generation costs, particularly gas. This can help mitigate the impacts of fossil fuel price spikes on energy prices, which disproportionately affect poorer households.
Strategies to decarbonize electricity supplies should also take account of the potential impacts of higher generation costs on those least able to pay. Extending the operation of existing reactors is one of the lowest-cost ways of producing low-carbon electricity.
2. Nuclear techniques help reduce pests and develop better crops
Worldwide, 822 million people are afflicted by malnourishment, approximately 9 million people die every year of hunger and hunger-related diseases. Every year up to 40% of crop yields and millions of livestock are lost due to pests and disease.
The sterile insect technique (SIT) uses ionizing radiation to sterilize specially bred male insects, which then compete with wild males to mate with females. The females that mate with the sterilized males produce infertile eggs, reducing the insect population. This technique has been used successfully to control two serious fruit fly pests, the Mexican fruit fly and Mediterranean fruit fly, as well as livestock-killing insects in sub-Saharan Africa.
The crop mutation technique can accelerate the process of breeding new crop varieties by using radiation to speed up and mimic the natural process of spontaneous mutation, the driving force behind evolution. In Peru, this technique led to improved barley and amaranth varieties that have adapted to climatic conditions in high altitudes. The new barley variety increases crop yields and contributes roughly US $32 million annually to the Andean farmers.
Food can be preserved for longer using irradiation. This technique can be used to kill pathogens such as E. coli, listeria and salmonella, as well as bacteria that would otherwise cause food to rot more quickly.
Nuclear technologies in food and agriculture improve the yield of crops, help reduce the losses due to pests and insects, and help maintain food fresh for longer, thus increasing the global available food supply.
3. Nuclear medicine helps tens of millions of people every year
Nuclear medicine is a critical component in diagnosing health problems related to the function of organs, tissues, or bones. Radioisotopes, which can be produced by nuclear reactors, are used as ‘tracers’ in PET scans, one of the most accurate means of detecting and evaluating most cancers.
Biotechnologists analyse specific molecules inside the body using nuclear materials. These techniques are an essential research component for chronic illnesses like AIDS and Alzheimer’s disease.
Radiation therapy (radiotherapy) can cure many different types of cancer, as well as other conditions, such as Graves’ disease (the most common cause of hyperthyroidism). In the case of cancer, most cancerous growths are sensitive to radiation.
There are numerous different treatment options, either with external or internal radiation, that can control or eliminate cancer by irradiating the area containing it.
The nuclear by-product cobalt-60 can kill off harmful and deadly bacteria, making it an effective solution to sterilize medical equipment, such as syringes and catheters.
4. Nuclear companies invest in training and education of their employees
Further education is part of new nuclear projects, whether in countries developing the skills of future staff for their first plants, or in countries with well-established nuclear programmes, seeking to train the next generation of employees.
In the UAE, the Energy Pioneers Program provides UAE nationals with the opportunity to gain specialist expertise and practical experience to pursue a range of careers across the country’s nascent nuclear energy industry. The UK, with a longestablished nuclear industry, continues to offer further education opportunities. Hinkley Point C, currently being built in the UK, has 1,000 apprenticeships during the construction phase.
The World Nuclear University has a mission to offer comprehensive leadership, communications, and technical training to support the next generation of nuclear leaders. It was founded by World Nuclear Association, the World Association of Nuclear Operators, the International Atomic Energy Agency, and the Nuclear Energy Agency.
The WNU has a worldwide network of nuclear education and research institutions offering training programmes for future leaders on nuclear energy, radioisotope production and applications of ionizing radiation in medicine and industry. Sponsorship by the IAEA enables students from emerging nuclear and developing countries to attend the WNU’s six-week Summer Institute course.
In countries, for example the US, nuclear plants create local tax revenue, which helps support a strong school system.
5. The nuclear industry is committed to improving the representation of women in the workforce at all levels
The role of reliable and affordable energy in the emancipation of women should not be underestimated. By powering domestic appliances, energy freed women and girls from menial labourintensive tasks many were compelled by societal pressures to perform, giving them more time to pursue other, more rewarding, activities.
But these benefits have not been universally available. If we are to achieve gender equity worldwide we must ensure all women have access to reliable electricity supplies, and that families have the economic resources to be able to purchase the domestic appliances that provide a better quality of life.
To have the highest-skilled workforce, an industry needs to attract the best talent from all genders. As with many industries in the science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) fields, women are under-represented in the nuclear industry, making up less than 25% of the workforce worldwide.
Globally, the “Equal by 30” campaign, a joint initiative between the International Energy Agency and the Clean Energy Ministerial, aims to accelerate the participation of women in the world’s clean energy transition and to close the gender gap in employment opportunities and earnings. Many companies in the nuclear industry have signed up to the initiative and made commitments such as strengthening the diversity of their teams and management, partner with schools to encourage young women to move into STEM careers or provide training to prevent discrimination and fight against bias.
6. Nuclear desalination provides clean water without greenhouse gas emissions
Clean and accessible water supplies are essential for economic development and human health. The World Health Organization predicts that by 2025, half of the world’s population will be living in water-stressed areas.
Desalination of water can address the challenges water-stressed areas face, but most desalination plants are powered by fossil fuels, resulting in the emission of greenhouse gases.
Nuclear reactors, in addition to providing electricity, can be a source of clean water. Nuclear reactors produce steam heat that drives turbines to make electricity, and leftover heat can be used to boil ocean water. The steam that condenses is clean, and the remaining salt can be returned to the ocean.
Nuclear science can also be used to clean water. The textile industry consumes huge amounts of water and chemicals, such as dyes, starches, acids, salts, and detergents. These would normally be treated chemically, creating secondary waste.
However, nuclear electron beam technology is used instead. The electron beams break apart the chemical bonds of clothing dyes and removes pollutants, allowing recycling of the water for reuse.
At one textile factory in Southern China the technique saves up to 4.5 million m3 of fresh water annually, equivalent to the water consumed by about 100,000 people.
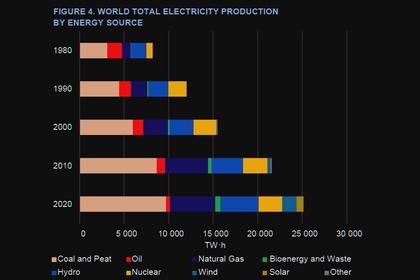
7. Nuclear power plants provide large amounts of clean, reliable, affordable energy
The use of fossil fuels for generating electricity has detrimental impacts on people and the environment, causing air, water, and soil pollution and producing large quantities of greenhouse gas emissions that drive climate change.
Sustainable development can be achieved only with access to clean, reliable and affordable energy. Energy is connected to all human activities and is the engine for economic sectors like agriculture, heavy industry, commerce and transport.
Nuclear power plants provide large amounts of clean, reliable, affordable energy and, regardless of the weather, can run for long periods of time without interruption. They are the ideal complement to wind, solar and storage for developing an affordable, reliable and low-carbon electricity grid.
In addition, through nuclear cogeneration, the heat generated by reactors can be redirected to power processes that are presently hard to decarbonize, such as domestic and industrial heating.
Nuclear projects are long-term investments and can operate for up to 80 years or more, making them cost-effective and affordable.
8. The nuclear industry provides well-paid, high-skill jobs and investment that supports local communities
The nuclear industry generates a broad range of jobs, including engineering, technical, and other specialist roles. For each 1,000 MWe of nuclear capacity constructed, some 200,000 job-years of employment are created. Nuclear sector pay tends to be higher than average, reflecting the specialist skills of the employees.
Nuclear energy projects also involve significant investment and regional infrastructure development, which contributes to economic growth and international exchange.
Nuclear energy projects increase gross domestic product growth in the short and long term. In addition, nuclear energy can have a positive impact on local employment, with a higher proportion of jobs being generated near to the location of the power plant than is the case with other low-carbon generation.
The nuclear industry helps to support jobs directly and indirectly.
For each direct job, approximately 2.5 to 3.5 indirect and induced jobs are generated.
9. Nuclear can supply the electricity and heat needed to support sustainable industrialization
Innovation is expanding the potential of nuclear technologies. The nuclear industry is pursuing the development of more efficient fuels that could enhance the performance of reactors currently in operation, as well as developing new reactor designs that will have a broader range of applications.
Industrial development is frequently energy-intensive. Nuclear reactors have the large output required to support such demand. In addition to the supply of electricity, high-temperature reactors will be able to replace fossil fuels as a more sustainable supply of process heat, with applications including the production of hydrogen.
New nuclear build projects support the many manufacturing companies in the supply chain that produce the components required for construction. Increasingly, new nuclear power projects are structured to support the local and host country supply chains, promoting more inclusive and sustainable industrial development. Once in operation, nuclear power plants continue to provide hundreds of high-skill employment opportunities for many decades.
Nuclear techniques can help make other industries more sustainable and safer. Nuclear non-destructive testing (NDT) is a quality-assurance procedure that helps verify the structural integrity of machines and materials without causing damage.
One such technique is industrial radiography, which is used to inspect welds.
10. Nuclear protects low-income households, which are disproportionately affected by volatile electricity prices.
The unequal access to energy within and among countries has considerable detrimental impacts on individuals and economies around the world, ranging from ambient air pollution to price shocks brought on by supply shortages.
Energy can – and has – been used as a political tool, and energy systems that rely heavily on imported fossil fuels are susceptible to external influence.
This often particularly harms the most vulnerable, individuals as well as countries. Nuclear energy can help to reduce these inequalities.
Uranium, which fuels nuclear reactors, can be found in abundance in many locations globally. Nuclear fuel can easily be stored onsite for many years, providing an insurance against potential supply issues. This diversified supply chain and ease of storage provides nations with greater control over their own energy systems, thus reducing the considerable inequalities that currently exist among countries.
Nuclear reactors also help to protect individuals against the price shocks that disproportionately affects low-income households. Whilst fuel costs for fossil-fired plants can make up a very large percentage of their overall costs – thus exposing consumers to extreme price changes – the fuel costs of nuclear power plants make up less than 10% of the overall cost, so variations in the cost of uranium have a much smaller impact on overall generation costs. This means that nuclear energy also can help reduce inequalities by protecting low-income households from disproportionately paying for market volatility.
11. Nuclear helps make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
Governments around the world are introducing policies to phase out internal combustion engines as the power source for road transport and encourage the use of electric vehicles that will avoid the direct emissions currently produced by petrol or diesel.
However, if the electricity used for transport is produced using fossil fuels this will still result in air pollution, such as smog and ozone, as well greenhouse gas emissions.
A sustainable shift to electric vehicles will increase demand for clean energy, including nuclear energy. With overnight charging likely to be a popular choice, the high availability of nuclear power plants will be an important factor.
Hydrogen fuel cells may also have a significant role to play in future transport systems. Again, it will be essential to produce hydrogen from clean energy sources. Nuclear reactors can already be used to produce hydrogen by electrolysis, and hightemperature reactors will be able to produce hydrogen through thermochemical techniques.
Heating homes with low-carbon alternatives will also contribute to meeting the goals of SDG11. Low-carbon hydrogen could replace natural gas in central heating boilers or greater use could be made of electric storage heaters.
For smaller and remote communities, small modular reactors are well-suited to provide clean electricity and heat.
12. Nuclear reactors produce the electricity needed to meet global energy demand responsibly
Many of the production and consumption patterns of the modern world are not sustainable.
Consumption and production must be carried out in a way that enables everyone to access a quality of life that allows them to realize their ambitions. At present billions of people are denied access to the type of lifestyle that has been enjoyed by developed countries for many decades.
Nuclear has already played a vital role in addressing this. Nuclear power has much lower raw material requirements per
unit of electricity produced than other clean energy options. It also produces large amounts of electricity from an energy-dense power source, using a fuel that has the potential to be recycled through reprocessing or novel nuclear fuel cycles.
Nuclear technologies can also help to make other sectors more sustainable. Cotton is well-known for requiring a lot of water, but scientists have used nuclear techniques to develop an enhanced cotton plant that increases yields by at least 30%, which could help reduce the amount of water needed.
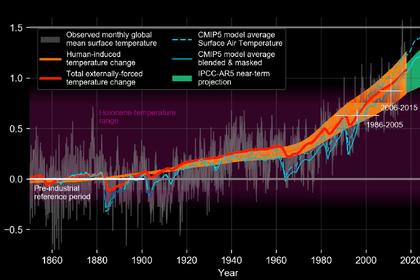
13. Nuclear energy is making a massive contribution to combating climate change
The impacts of climate change can already be seen, from exacerbating global poverty, water scarcity and food insecurity to severely impacting public health due to the spread of diseases, extreme weather events and the destruction of ecosystems.
By 2030, it is estimated that more than 100 million people will be forced into extreme poverty and some 250,000 additional deaths every year between 2030 and 2050 will be caused by climate change.
Nuclear energy has one of the smallest carbon footprints of all energy sources, and it is one of the largest low-carbon electricity generators globally. The use of nuclear power avoids more than two billion tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions every year, the equivalent of removing half of the world’s 520 million vehicles.
Nuclear energy can be deployed at the rates required to avoid the worst effects of climate change. This has been seen in countries such as France and Sweden, where a rapid expansion of nuclear power in the 1970s and 1980s contributed to a high degree of decarbonization of their electricity systems, whilst delivering substantial economic growth.
14. Using nuclear energy avoids the emissions that cause ocean acidification
Marine biodiversity is in significant decline across the world as a direct result of human activity. Ocean acidification caused by fossil fuels has detrimental impacts on marine life and poses an especially big threat to coral reefs around the world. Coral reefs are the nurseries of the oceans and more than 25% of all marine life depend on them, despite occupying less than 1% of the ocean floor. It is estimated that they provide food to hundreds of millions of people, and supply resources and services (including jobs, food, and protection from storms and erosion) worth more than $375 billion every year.
Nuclear power can play a major role in reducing ocean acidification and thus protect the immense biodiversity of the oceans, thanks both to its low-carbon credentials and the fact that it does not cause chemical emissions that pollute waterways – unlike many other energy sources.
Nuclear and isotopic techniques can also help understand aquatic ecosystems, assess pollution and verify the effectiveness of clean-up and remediation techniques. These techniques can also be used to evaluate past changes in ocean acidity, as well as the ocean’s capacity to store carbon and the potential impact this will have on the climate in the future.
15. Nuclear power plants produce large amounts of electricity from small land areas
Human activities have transformed the face of our planet. Unsustainable practices in activities such as fuel extraction and agriculture, as well as climate change, pose a significant threat to biodiversity across the world.
The world’s forests are central to keeping climate change in check as they absorb a third of all carbon dioxide emissions. However, logging, land degradation and desertification threatens forests worldwide, which in turn results in additional desertification, degradation and biodiversity loss. Forests can also be threatened by coal mining. The Hamabacher Forest in the west of Germany has been almost completely destroyed by mining for lignite, which emits particularly high levels of carbon dioxide when burned.
In comparison to other low-carbon energy sources, nuclear power requires the smallest amount of land per unit energy produced, leaving more undisturbed land for natural habitats.
Nuclear techniques can be used to assess soil quality and study how crops take up nutrients. This helps in the development of more efficient soil management and crop production methods.
Experts can also track and stop contaminants from harming the environment, by using nuclear science to identify certain isotopes in different contaminants to measure their concentration and trace their source.
16. The Non-Proliferation Treaty promotes cooperation on the peaceful uses of nuclear technology
National nuclear power programmes contribute to peace. The development of national nuclear power programmes plays a key role in the non-proliferation of nuclear weapons.
In return for access and cooperation on the peaceful uses of nuclear technology, countries that have signed the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) undertake to not pursue a nuclear weapons programme.
Compliance with the NPT is verified through inspections carried out by the International Atomic Energy Agency, ensuring that fissile material in NPT signatory countries is not diverted for weapons use.
Nuclear techniques can also help enhance security in other fields. Neutron scanning devices can be used to detect explosives, drugs or weapons, with applications in airport security, forensics and crime scene investigation.
17. Nuclear organizations work with stakeholders to help meet the Sustainable Development Goals
Strong partnerships between the nuclear industry and other stakeholders enable nuclear technologies to contribute to meeting the Sustainable Development Goals. A key partnership in Canada is the Darlington and Bruce refurbishment projects, a collaborative effort between the nuclear industry and the Government of Ontario. This effort will ensure the life extension of 10 reactors. The refurbishment project, which will last approximately 15 years, is creating thousands of jobs and extending the operating lifetime of the reactors for another 30 years or more.
Launched in June 2021, the IAEA’s “Nuclear Saves” Partnerships provide an opportunity for companies and organizations to support the IAEA in transferring nuclear science and technology to countries to improve the health and prosperity of millions of people around the world. The Nuclear Energy Institute, World Nuclear Association and Westinghouse Electric Company are Nuclear Saves partners with the IAEA.
The nuclear industry conducts outreach with developing countries, and has partnerships with governments, NGOs and UN bodies such as the IAEA and UNECE. One example is the International Framework for Nuclear Energy Cooperation, which is a partnership of countries that share knowledge and experience with developing countries so that they can make informed decisions regarding the establishment of nuclear facilities.
-----
Earlier: