GERMANY'S COAL REFUSAL

By SIMON GOESS Freelance Energy Market Analyst SG Consult
Originally published here and co-authored by Lydia Bischof
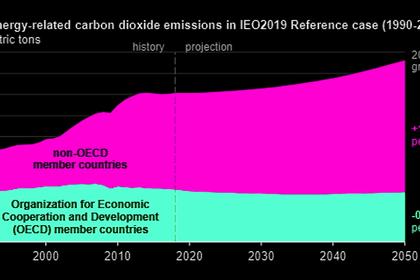
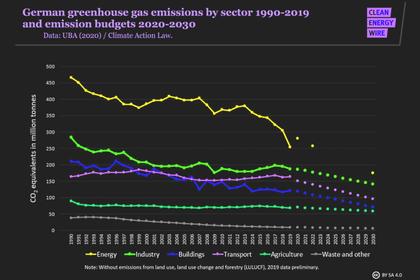
ENERGYCENTRAL - May 19, 2021 - The German federal government published its updated Climate Protection Act on May 12, 2021. According to this, the energy industry in particular should shoulder a greater reduction in CO 2 emissions and reduce its emissions to 108 instead of 175 Mt CO2 equivalents by 2030. In a current calculation, the energy market experts from Energy Brainpool are analyzing how the new sector target can be achieved and what role the coal phase-out and the expansion of renewable energies (RE) play in this.
The main results:
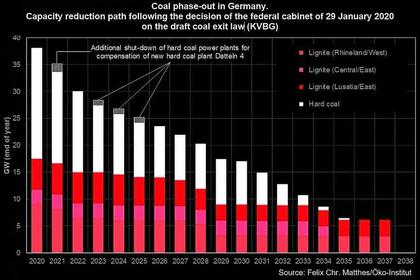
Electricity market scenarios for target achievement: The energy industry's new sector target for 2030 can only be achieved by bringing forward an exit from coal. The reduction in coal-fired power generation remains by far the greatest leverage in terms of emissions. If the phase-out of lignite alone is brought forward to 2029, the envisaged share of renewable energies in gross electricity consumption must be increased from 65 to 75 percent in 2030. If the coal phase-out were also brought forward to 2029, the energy sector target could also be achieved with a renewable share of 65 percent. Michael Claußner, Expert at Energy Brainpool, says: “A low share of renewables in electricity consumption inhibits emission reductions, especially in sectors such as transport, hydrogen or heating, which are linked to the electricity market. Because flexible consumers would draw electricity especially in the windy and sunny hours ”. - more intensive than with 75 percent EE content.
Security of supply: If the lignite phase-out is brought forward, around 11 GW, and if the coal phase-out is fully brought forward, around 16 GW of additional flexibility is required on the electricity market in order to guarantee security of supply. This flexibility can be provided by storage technologies, demand-side management, additional gas-fired power plant capacities and the network reserve. The higher the share of storage or demand-side management, the lower the emissions.
Role of wind and solar energy in transition: The role of the electricity producers of energy from RE is changing increasingly: from the displacer of fossil electricity generation to the enabler of emission savings in coupled sectors. In the periods in which wind and solar systems are producing, there will be less and less fossil-based residual electricity generation in the future. This could be displaced by even more wind and solar additions. Instead, these surpluses are increasingly being used in other sectors (e.g. transport, hydrogen production, heat supply) or exported in order to displace fossil electricity producers in neighboring countries. The contribution of the additional RE expansion to the achievement of the energy industry sector target with high RE shares shrinks. Instead, the contribution is growing in other sectors in order to achieve the goal. Michael Claußner adds: -intensive electricity generation. "
-----
This thought leadership article was originally shared with Energy Central's Generation Professionals Group. The communities are a place where professionals in the power industry can share, learn and connect in a collaborative environment. Join the Generation Professionals Community today and learn from others who work in the industry.
-----
Earlier: