CHINA CLIMATE CONTROL

PLATTS - 27 Jan 2022 - China's current "dual control system" used to control energy consumption and energy intensity will eventually be transformed into a "dual control system" for carbon emissions and carbon intensity, President Xi Jinping said in a speech delivered at a session of the Political Bureau of the Communist Party of China.
A transcript of the speech, made on Jan. 25, was posted by the National Energy Administration on its website. These were some of the most detailed comments made by Xi on his view of China's decarbonization since climate pledges of carbon peaking in 2030 and carbon neutrality in 2060 were first announced.
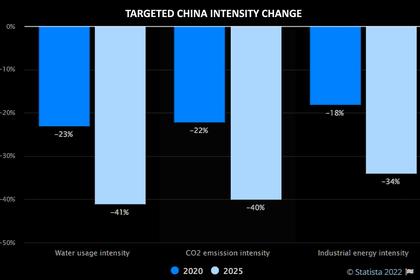
China currently implements a "dual control mechanism" under which provinces are given targets for total energy consumption and energy intensity, which is the amount of energy consumed for each unit of GDP growth.
The system has been used to cut energy consumption most recently in 2021, and Xi said it will eventually be deployed to control emissions and carbon intensity, which is the volume of emissions per unit of GDP growth.
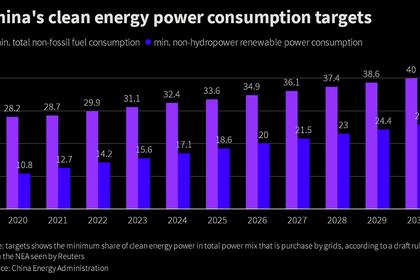
Xi said energy consumption from renewable sources will not be capped and controlled under the dual control mechanism, and a uniform mechanism for carbon emission statistics and verification will need to be established to implement carbon-based dual controls.
Such a transformation will also be supported by a more comprehensive set of rules and regulations, as well as taxation, pricing, investment and financing policies, Xi said.
Balancing energy transition
Xi called for a well-coordinated energy transition that balances economic development and energy security, with alignment between "a capable government" and "an effective market". He pointed out the bottlenecks and dilemmas faced by China in its decarbonization pathway and proposed countermeasures.
"Cutting emissions does not mean cutting productivity or eliminating all emissions," he said, adding that China must strike a balance between emission reductions, energy security, supply chain security and food security, without disrupting people's lives.
"The coordination between national and regional policies must be ensured, and the 'one-size-fits-all' approach should not be adopted," Xi said.
China's provinces are at different stages of economic and industrial development and require realistic, localized action plans that allow different regions to realize carbon peaking and neutrality at a different pace.
Future power system
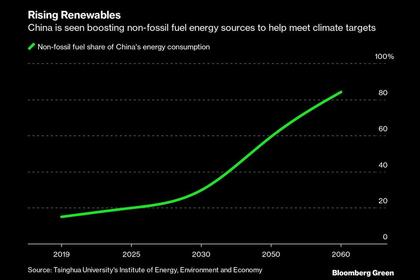
Xi said large-scale solar and wind will lay the foundation for China's future power system, supported by high efficiency coal-fired power plants, and an ultra-high-voltage electricity transmission system for cross-regional supply to boost renewables' utilization rates.
China will gradually withdraw from fossil fuels while ensuring the safety of new energy sources, Xi said. He said coal consumption growth needs to be regulated "in a strict and reasonable manner", while domestic production of crude oil and natural gas is expected to steadily increase to reduce import dependency.
Xi said the government and market forces must work together to develop a comprehensive incentive and control mechanism that motivates carbon peaking and carbon neutrality, but at the same time control the blind development of emission-intensive, energy-intensive, and low-quality projects.
Meanwhile, the government is expected to push traditional industrial sectors like steel, non-ferrous metals, refining, chemicals and building materials to upgrade, accelerating the digitization and low-carbon transformation, Xi said.
Xi said China also needs a long-term strategic view instead of quick wins in its decarbonization journey, which should be gradual and persistent.
"China's decarbonization should fully leverage market mechanisms. The current carbon pricing mechanism will be improved, and the carbon market will be aligned with electricity markets and energy consumption rights," he said.
-----
Earlier: