U.S. DIGITAL GRID INNOVATIONS

By ANTHONY ALLARD Executive Vice President, Head of North America Hitachi Energy
ENERGYCENTRAL - May 24, 2022 - The Biden Administration’s Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) is intended, at a high level, to improve U.S. infrastructure, mitigate climate change, and modernize our country’s energy systems – in the process, it’s also expected to create jobs. One particular component of the IIJA, Section 40107, presents a unique opportunity to help utilities and other participants in the energy system embrace innovation and pioneer new technologies and practices that can enable them to modernize and strengthen their operations.
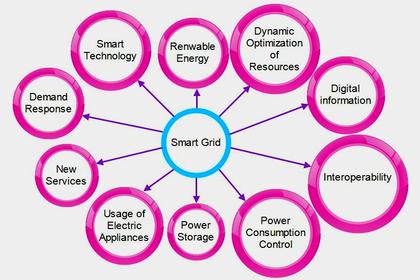
How can this be accomplished? A key focus of 40107 is around the digitalization of utilities and encouraging investment in new technologies, like smart grid capabilities and utility analytics, that can lead to faster, more intelligent, and automated decision-making and promote resiliency. Section 40107 also supports exploration into emerging challenges, such as the integration of large-scale EV charging infrastructure (and associated loads) into grids.
Overcoming Hesitation from Utilities
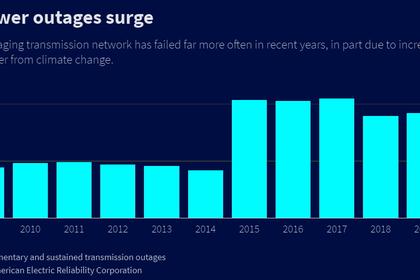
Often, utilities don’t like to take risks because energy is a critical resource on which society depends and their overarching responsibility is to provide a high-quality, consistent power supply. Any unplanned outages or interruptions in service are extremely unwelcome and potentially very disruptive to local communities. As a result, many utilities simply aren’t prepared to try out ‘new’ technologies or allocate capital from another important project.
That said, with the challenges facing utilities – integration of ever-increasing volumes of renewable energy, introduction of large-scale EV charging requirements, growing cyber-security risk – there is a great deal of work to be done to improve utility operations while accommodating these shifting industry dynamics. Specifically, utilities will have to upgrade their capabilities for gathering, analyzing and utilizing data in operational systems, reporting systems, management systems and more.
Section 40107 of the IIJA provides a mechanism to enable utilities to invest in new technologies that could address some of these challenges, while minimizing risk and partially subsidizing their investments.
Supporting Innovation with Policy: Understanding Section 40107 of the IIJA
Section 40107 of the IIJA presents a major opportunity to encourage innovation by utilities. It establishes a system of matching grants, which can enable utilities to explore new technologies or novel applications of existing technologies through large-scale demonstrations or pilots, or targeted commercial deployments, with the U.S. government covering a significant portion of the needed funding.
The program will utilize a mechanism known as the Smart Grid Investment Matching Grant Program, developed as part of the American Reinvestment and Recovery Act (ARRA), a program instituted in 2009. This mechanism is already familiar to many potential applicants, which should help to simplify the application process.
There are a number of broad categories of technologies, software and applications within the scope of Section 40107, including:
-----
This thought leadership article was originally shared with Energy Central's Utility Management Community Group. The communities are a place where professionals in the power industry can share, learn and connect in a collaborative environment. Join the Utility Management Community today and learn from others who work in the industry.
-----
Earlier: