U.S. SMART GRID INNOVATION
By ANDREW BRAEGER Data Services Manager Tacoma Public Utilities
ENERGYCENTRAL - May 24, 2022 - The so-called “four D’s” of energy disruption have served as a helpful way to describe the energy transition taking place, namely, decarbonization, democratization, decentralization, and digitalization.
There are various grid architecture representations of how the utility model of the future may come to life. Some models portray the electric utility as nearly entirely removed from the image altogether. Other models depict the utility as the steward of the poles and wires, that is, the transmission and distribution systems.
My perspective is that the traditional model of utility vertical integration or equivalent, especially in the Pacific Northwest, still serves as an optimal solution for providing equitable, affordable, and reliable energy for all customers.
Further, the next evolution of this traditional energy model can support the innovative application and development of new products and services to provide enhanced energy services with greater flexibility, resiliency, sustainability, and customer affordability.
This traditional energy delivery model must evolve to support two essential foundations:
- Optimized utility-owned grid capabilities
- Two-way integration that supports distributed grid capabilities
Utility-owned Grid Capabilities
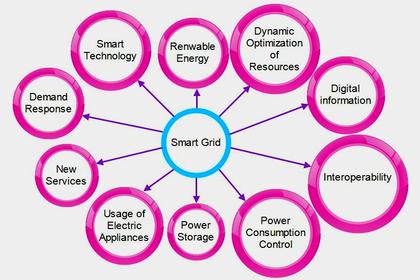
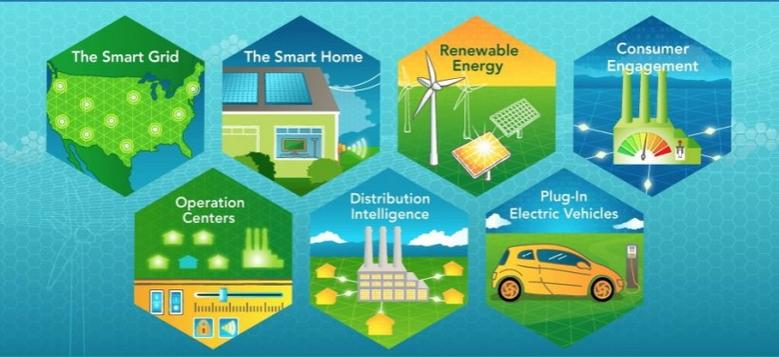
The utility model of the future continues to maintain a level of centralization and coordination. Utilities, however, must modernize these centralized capabilities to ensure continued customer access to affordable, reliable, resilient, secure, sustainable, and flexible energy services. This is the massive opportunity of grid modernization and includes strategic planning and investment in next-generation utility capabilities, including distribution automation, green hydrogen for generation and storage, utility-operated microgrids, new rate options for customers, just to name a few.
Distributed Grid Capabilities
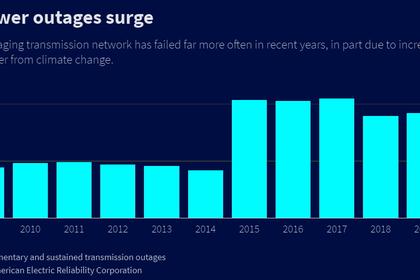
Further, the electric grid of the future is not just centralized, but flexible enough to support distributed grid capabilities. Many of these disruptors have been coming online for some time, such as customer-owned solar, net metering, and electric vehicles. In response to the threats of climate change, volatile weather, and wildfires, the next ten years will see a dramatic increase in community-owned microgrids, customer-side resiliency capabilities supported by electric vehicles and customer-owned solutions, and distributed green hydrogen generation and storage.
Building the clean energy future
Utilities must start planning now for the technology and internal capability solutions needed to support a flexible grid that provides centralized and distributed energy capabilities.
Technology solutions needed to support this flexible energy model include:
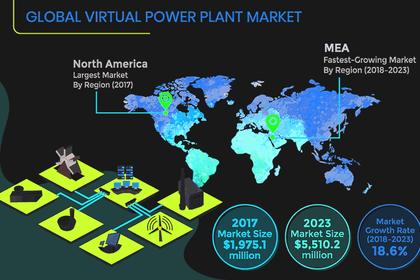
- Distributed energy resource management system platforms or virtual power plants
- GIS for digital twin representation of centralized and distributed utility operations
- Asset performance management solutions for power equipment optimization
- Advanced distribution management system platforms (ADMS) for distribution automation
- Customer-facing demand side management and home energy management platforms
Enabling innovation thru technology
Utilities have traditionally approached technology solutions like advanced metering infrastructure and GIS as solutions for improving operational efficiency. The most progressive utilities, however, recognize that technology solutions serve as the building blocks necessary for enabling the innovative utility use cases of the future, both known and unknown opportunities.
A utility after completing a flexible ADMS deployment coupled with strong GIS integration, for example, can leverage the solution not only for traditional distribution automation, but integration of distributed energy resources coming online, such as electric vehicles, community-owned microgrids, or residential solar installations.
To realize these benefits, utilities must consider future use cases and architect technology platforms with flexibility and agility in mind to enable innovative industry applications.
Simply put, while the four D’s may operate as a helpful symbol for describing the industry disruptions at play, the complete picture is a bit more complicated and includes elements of traditional utility-owned centralization and distributed energy management as forces in enabling an innovative energy future.
-----
This thought leadership article was originally shared with Energy Central's Grid Professionals Community Group. The communities are a place where professionals in the power industry can share, learn and connect in a collaborative environment. Join the Grid Professionals Community today and learn from others who work in the industry.
-----
Earlier: