DECENTRALIZED RENEWABLE ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES
By NIMESHEE SINGH CEO, Ruvexa Enterprises
ENERGYCENTRAL - Jan 9, 2024 -
Introduction
In recent years, the global energy landscape has witnessed a remarkable revolution, with decentralized renewable energy (DRE) emerging as a promising solution to meet our increasing power demands sustainably. Unlike traditional centralized power systems, decentralized renewable energy focuses on generating electricity through localized renewable sources. This article aims to shed light on the importance and advantages of decentralized renewable energy, particularly in remote and rural areas where grid connectivity is challenging.
What is decentralized renewable energy?
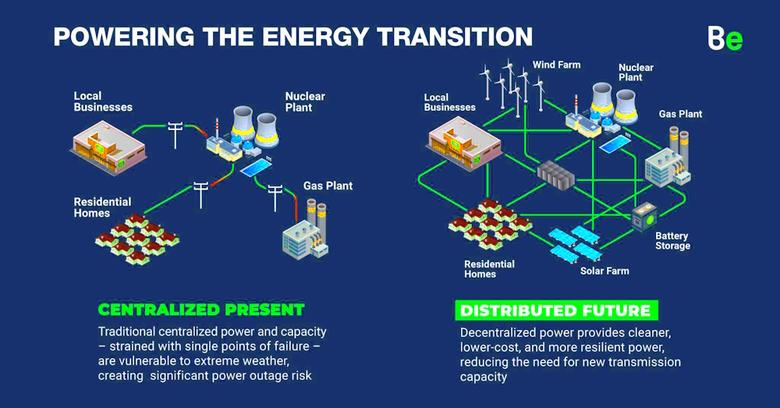
Decentralized renewable energy generation refers to the process of producing electricity from renewable sources on smaller, local levels, as opposed to centralized power plants. It involves harnessing the power of renewable resources such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass through distributed energy systems. These decentralized systems allow for the generation of electricity closer to the point of consumption, reducing dependency on long-distance transmission and enabling communities to become self-sufficient.
Breaking the Chains of Traditional Power Systems
Decentralized renewable energy breaks away from the long-established model of centralized power systems, which heavily rely on fossil fuels and transmitting power over vast distances. Instead, it harnesses the abundant energy from renewable sources through smaller-scale installations. This shift allows communities to become self-sufficient and frees them from the vulnerability of centralized grid networks.
Energy Accessibility through Resilient and Reliable Energy Networks
One of the major advantages of DRE lies in its ability to create resilient and reliable energy sources. Decentralized renewable energy provides a localized solution in remote and rural areas, where grid connectivity is often unreliable or prohibitively expensive. By generating electricity closer to the point of consumption, communities can enjoy continuous power supply, reducing dependence on external sources and mitigating the impact of natural disasters or grid failures.
Furthermore, energy poverty is a grave concern in many regions worldwide, especially in remote and rural areas. DRE can serve as a significant catalyst in bridging this gap by bringing affordable and sustainable power solutions to those who need it the most. By facilitating local energy generation, communities gain control over their energy supply, unlocking a world of opportunities for education, healthcare, economic growth, and improved quality of life.
Fostering Environmental Sustainability
The transition to decentralized renewable energy not only offers social and economic benefits but also contributes to a greener and cleaner future. By tapping into renewable sources, we reduce reliance on fossil fuels, limiting carbon dioxide emissions and combating climate change. Moreover, decentralized renewable energy projects can be tailored to the unique local ecosystems and minimize environmental impacts, ensuring a sustainable coexistence with nature.
Economic Empowerment
DRE projects have tremendous potential to stimulate local economies. By investing in renewable infrastructure, communities can create jobs, attract investment, and foster entrepreneurship. Local sourcing of materials, installation, and maintenance services also generate economic opportunities, bolstering the overall development of rural and remote areas.
Challenges in Implementation
While decentralized renewable energy holds great promise, several key challenges must be addressed for successful implementation. These challenges include:
- Technological Challenges
The biggest hurdle in DRE implementation is the lack of robust and commercial-ready renewable energy technologies that can be implemented on a wide scale. One potential solution is to use a mix of various renewable energies such as solar, wind, biomass, etc. based on the available resources in an area. However, there is still significant research and development needed to ensure a robust energy network.
- High Initial Infrastructure Costs
Implementing decentralized renewable energy systems requires upfront investments in infrastructure such as solar panels, wind turbines, or small-scale hydropower facilities. These initial costs can be a barrier, particularly for communities with limited financial resources. However, it is important to note that as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved, the costs of renewable energy systems are decreasing, making them more accessible over time.
- Energy Storage Technologies
Reliable and cost-effective energy storage technologies are essential for decentralized renewable energy systems to provide round-the-clock power. While significant progress has been made in energy storage solutions like batteries, pumped hydro storage, and thermal energy storage, they are not yet available at fully commercial scales. Continued research and development in energy storage technologies are crucial to overcome intermittency and ensure a stable energy supply from decentralized sources.
- Integration with Grid Networks
Integrating decentralized renewable energy systems into existing grid networks can present technical complexities. Ensuring seamless interaction between decentralized energy generation and centralized grid infrastructure requires robust planning, smart grid technologies, and grid management strategies to balance supply and demand.
- Regulatory Frameworks
The lack of supportive and clear regulatory frameworks is often a significant hurdle in the widespread adoption of decentralized renewable energy. This creates uncertainty and barriers for developers, investors and stakeholders involved in the sector. Policies and regulations need to be developed and implemented to promote the integration of decentralized systems into existing energy grids, incentivize investment, and ensure fair compensation for excess electricity generation. Furthermore, a framework for an energy marketplace needs to be set up for transactions of surplus energy between the nodes of the decentralized energy network.
Addressing these challenges will require collaborative efforts from governments, policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities. Through supportive policies, financial incentives, technological advancements, and capacity-building initiatives, the path to widespread adoption of decentralized renewable energy can be paved.
Conclusion
Decentralized renewable energy stands as a transformative force, offering innovative and flexible solutions to meet energy needs sustainably, especially in remote and rural areas. It enhances community resilience, reliability, and independence by shifting from centralized power systems to local renewable sources. While ushering in a greener and more sustainable future, it serves as a catalyst for social, economic, and environmental change, empowering communities in myriad ways.
Despite the numerous benefits, challenges such as regulatory frameworks, infrastructure costs, and technological advancements must be addressed. By tackling these challenges head-on, we can accelerate the transition to a decentralized renewable energy landscape, ensuring a brighter, more equitable tomorrow for all. This transformative energy revolution, if implemented with the right planning, can enable a move towards a decentralized, sustainable energy future.
-----
This thought leadership article was originally shared with Energy Central's Clean Power Community Group. The communities are a place where professionals in the power industry can share, learn and connect in a collaborative environment. Join the Clean Power Community today and learn from others who work in the industry.
-----
Earlier: